कट फ्लावर की कटाई के बाद देखभाल या हैंडलिंग कैसे करें।
In agriculture, post harvest handling is the stage of crop production immediately following harvest, including cooling, cleaning, sorting and packing. Post-harvest treatment largely determines final quality, whether a crop is sold for fresh consumption, or used as an ingredient in a processed food product.
The most important goals of post-harvest handling are to keep the product cool, to avoid moisture loss and slow down undesirable chemical changes, and avoiding physical damage such as bruising.
Initial post-harvest storage conditions are critical to maintain quality. Each crop has an optimum range for storage temperature and humidity. Also, certain crops cannot be effectively stored together, as unwanted chemical interactions can result.
Various methods of high-speed cooling, and sophisticated refrigerated and atmosphere-controlled environments, are employed to prolong freshness, particularly in large-scale operations.
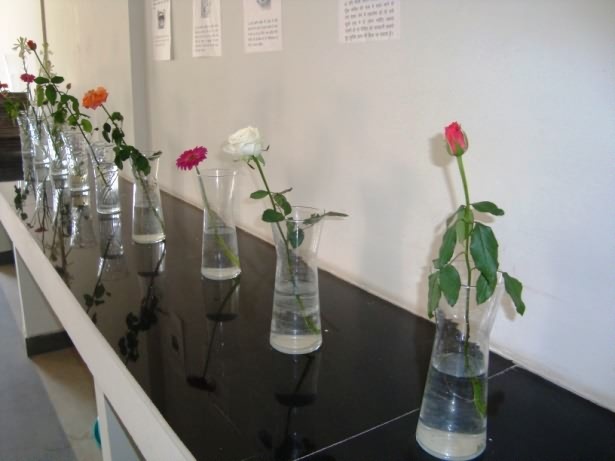
Vase Life of cut flowers:
A fresh flower is still a living specimen even though it has been cut from the plant. The vase life of cut flowers decline due to the following reasons.
- Inability of stems to absorb water due to blockage
- Excessive water loss from the cut flower
- A short supply of carbohydrate to support respiration
- Diseases
- Ethylene gas
- Room temperature and humidity
Preservatives are used to extend the vase life of cut flowers. Floral preservatives are very effective in maintaining quality and extending longevity. We can have almost double vase life by using preservatives in water as compared with no preservatives.
Floral preservatives perform three functions:
- Provide sugar (carbohydrate).
- Supply a bactericide to prevent microbial growth and blockage of the water- conductive cells in the stem.
- Acidify the solution
Some of the preservatives used in floriculture are:
- Aluminium Sulphate (Also4)
- T.S. (Silver Thio Sulphate) Solution
- Chlorine: Chlorine it is added 20 mg/liter.
- Rvb Chrysal : Rvb Chrysal preservative is used @ 2 ml/liter. Every bucket containing 5 to 7 liters water. We should add 10 to 15 ml of Rvb Chrysal.
- Florissant: Florissant buffer stock solution of 8 liters is prepared by adding 1 liter of Florissant and 7 liter water. Later added to every bucket containing 5 to 7 liter water. Florissant is available in a convenient pack of 1 litre, 5 litres, 10 litres, 25 litres and 200 litres.
Water should be treated with any of the above mentioned preservatives and then flowers should be put into the bucket.
Testing vase life of flowers is nothing but checking the life of harvested flowers from the day of harvest to the final drooping after full open. Following steps are to be followed.
- Take two containers or glass bottles named containers A and container B.
- Container A container pure water with EC < 0.5 and pH – 5.5 to 7.
- Container B contains water and preservative in desired quality.
- The quantity of water should be half of the container size. Generally the height of the container should be 30 to 40 cm and diameter around 10 to 15 cm.
- Select two stems of same length, bud size, bud opening of the same variety. Cut the bottom of the stem 1 cm and keep in the containers.
- Keep the stems in containers.
- Everyday cut the bottom of the stems by 4 cm and keep it again in the same container.
- Every alternate day replace water and water with preservative.
- The experiment should be carried out at room temperature and normal humidity with enough light.
- Continue the procedure till both the stems are fully open and get dropped.
- Count the number of days since the start of experiment and that is the vase life of the flowers. Such experiment should be carried out for different varieties in different seasons.
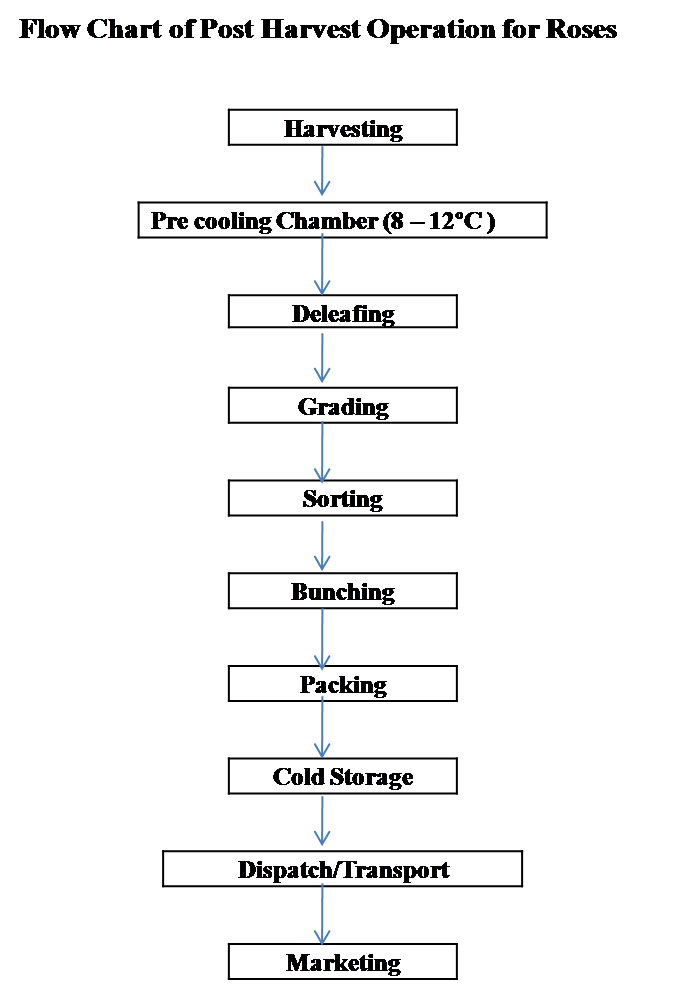
1. Post Harvest Operations of Rose
1. Harvesting :
Harvesting is the last but not least operation is the greenhouse. Harvesting should be done at right stage and right time. Harvesting should be done by skilled labour
2. Pre Cooling Chamber :
The Buckets contains 70 - 80 stems are shifted from greenhouse to pre cooling chamber at an earliest and kept at 8 – 120C for at least 2 hours. This is done to remove field heat and extend the storage life of flowers.
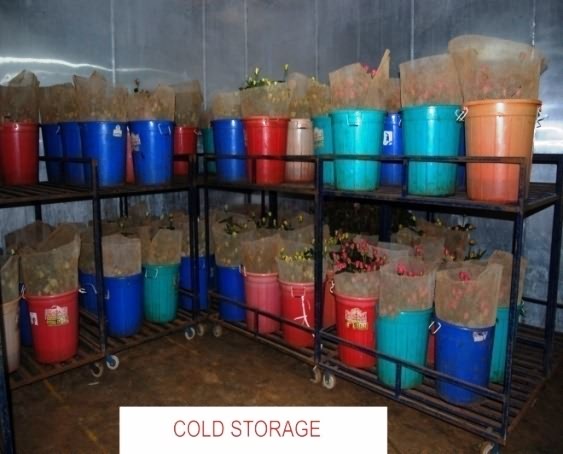
Cold storage for Rose
3. Deleafing :
The leaves from the lower portion of the stem are removed upto 15 cm to reduce the weight of the stem. All infected leaves are also removed. The disposal of the leaves from the Deleafing machine area should be done frequently. The rubber brushing should not be too hard as it may damage the stem.
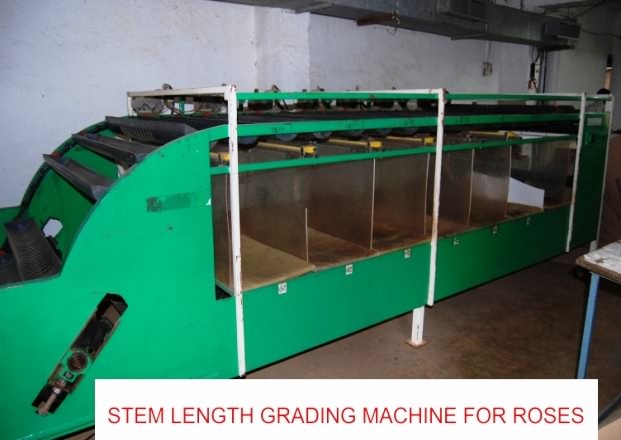
4. Grading:
The grading of flowers should be done according to the stem length, bud size, stem thickness and opening of flowers. In manual grading, skilled workers are used for grading. Bent neck, thorn damage flowers, disease and pest affected and thick stem should be rejected.
Rose stem cutting blade
5. Sorting and Bunching:
Criteria for sorting of flowers as follows -
- Sorting should be done according to local and export market requirement.
- Thickness of the stem should be uniform in a bunch.
- All the buds in a bunch should have same opening stage.
- Bunching is done according to buyers requirement viz staggered or level head bunching.
Table: General specification for number of stems per bunch
| S.No. | Country | Number of stems in a bunch | Type of bunch |
| 1 | Domestic market (India) | 20 | Staggered |
| 2 | Japan | 10 | Level head |
| 3 | Europe | 10 | Level head |
| 4 | Germany/ Holland/ Dubai | 20 | Staggered |
6. Cold Chain :
It is very important to maintain the same cut stage of flowers the post harvest operations right from harvesting in the field upto the flower reaching to the market. If the temperature is not maintained properly the flowers may open and the price is reduced to a great extent.
Hence the temperature in the post harvest chain is reduced to minimize the activities in the stem. The temperature is reduced during post harvest as follows:
Table: Cold chain temperatures at different stages
| S.No. | Location | Temperature | Minimum Holding Time |
| 1 | Green house at the time of harvest | 24°C | Immediately |
| 2 | Packing room | 18°C | One Hour |
| 3 | Pre cooling | 8°C to 12°C | Two Hours |
| 4 | Cold storage | 0°C to 2°C | Two Hours |
| 5 | Reefer Van | 0°C to 2°C |
7. Packing
Step No. 1.
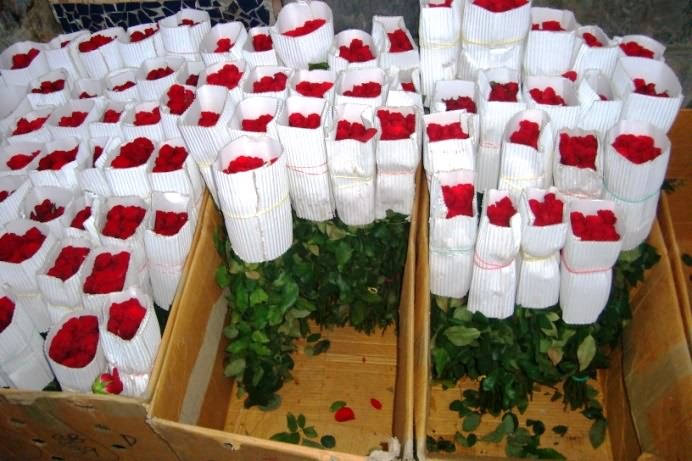
After bunching the flower heads are wrapped with white or brown coloured wrappers. The size of the wrappers depends upon the bud size and number of flowers per bunch.
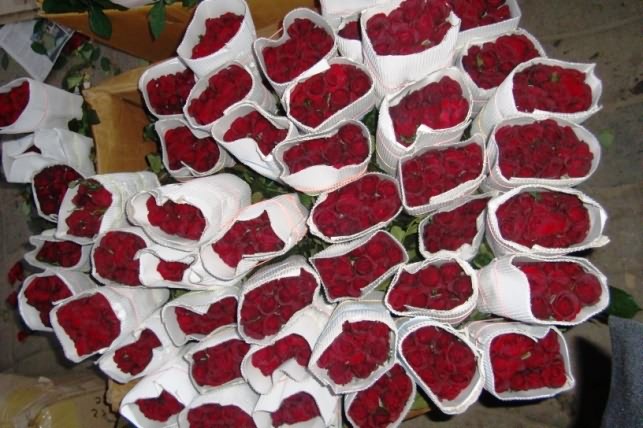

Rose packing in head wrap
Table: Wrapping of Roses
| S.No. | Stem Length (cm) | Bud Size (cm) | Wrapper Size (cm) |
| 1 | 40 | 3 | 20 X 35 |
| 2 | 50 | 3.5 | 20 X 40 |
| 3 | 60 | 4 | 20 X 45 |
Step No. 2.
Two rubber bands (2” or 4”) are placed below the bud and at the bottom of stems to avoid loosing of stem or wrapper during transport.
Step No. 3.
The size of the packing box varies with the stem length, number of stem and distance of the destination where the flowers are to be sold. Generally 3 ply corrugated paper box is used for domestic market and 5 ply corrugated paper box is used for export purposes.
Table: Packaging of Roses in Corrugated boxes
| S. No. | CorrugatedBox Size | Stem length | ||
| 40 cm | 50 cm | 60 cm | ||
| 1 | 100 x 40 x 20 cm | 600 | 500 stem | 400 stem |
| 2 | 100 x 40 x 21 cm | 600 | 500 stem | 400 stem |
A printed corrugated box carries following information
- On top side of the lid “Fresh cut flower “is printed.
- On width wise side of the lid “Variety, number of stems, stem length, box number is written on both sides.
- On length wise side of the lid “Fresh cut flower and handle with care is written on both sides.”
- Senders and buyers address with phone number.
Step No. 4.
Bunches are packed in 5-ply boxes in such a way that flower heads face in opposite direction. Bunches should be placed in a row along the length of box. The second layer is placed opposite to the first layer.
Step No. 5.
Each layer of bunches is covered with soft paper.
Step No. 6.
Once bunches are placed properly in a box strapping is done, the box is closed with the lid and strapped properly. The stem should be tightly held in the boxes so that they are not subject to jerk movements during transport.
Step No. 7.
The boxes are kept in cold storage at 0 – 20C till dispatch.
Rose Packaging in Corrugated boxes
 8. Transport
8. Transport
A common rule should be followed “first in, first out” i.e. first arrived flowers from green houses should be processed and dispatched first.
Reefer van containers are generally used to transport cut flowers for export. These vans transport the produce from the production center to the airport and to the concerned market.
0°C to 2°C temperature is maintained inside the reefer van.
- Flowers with more than 35 cm are sold at local market.
- Bend neck and bull head buds should be rejected and sold as loose flowers.
- Cut flowers having no or less infestation of disease and pest fetch good price in local market.
- Roses are sold generally in 20 stems/ bunch (staggered head) in local market.
Table: General Quality parameters of roses for domestic and export markets
|
S.No. |
Stem length (cm) |
Bud size (Length) (cm) |
Bud diameter (cm) |
|
1 |
40 |
3.2 |
2.2 to 2.5 |
|
2 |
50 |
3.5 |
2.5 to 2.7 |
|
3 |
60 |
3.5 to 4 |
2.7 |
|
4 |
70 |
4 |
2.7 |
Table: Weight of the export quality bunches
|
S.No. |
Stem length (cm) |
Weight / stem(gm) |
Weight of bunch of 20 stems (gm) |
|
1 |
40 |
15 – 18 |
300 – 360 |
|
2 |
50 |
30 – 35 |
600 – 700 |
|
3 |
60 |
45 |
900 |
2. Post Harvest Operation of Carnation
1. Harvest
The flower are kept in clean buckets after harvesting and sent to the packing hall.
2. Grading
Grading is done according to the stem length of carnation. The damaged, pest and disease infested stems should be rejected. Minimum 40 cm stem length for domestic market and minimum 60 cm for export market are recommended
3. Sorting
Same bud size and same opening sage in carnation cut flower are sorted together.
4. Packing
The flowers are packed in bunches and sleeves or paper sleeves, according to demand of the buyer. The standard carnation is packed in a bunch of 20 flowers and spray carnations of 10 flowers. Printed corrugated boxes carries following in formation
- On top side of the lid “Fresh cut flower “is printed.
- On width wise side of the lid “Variety, number of stems, stem length, box number is written on both sides.
- On length wise side of the lid “Fresh cut flower and handle with care is written on both sides.”
- Senders and buyers address with phone number.
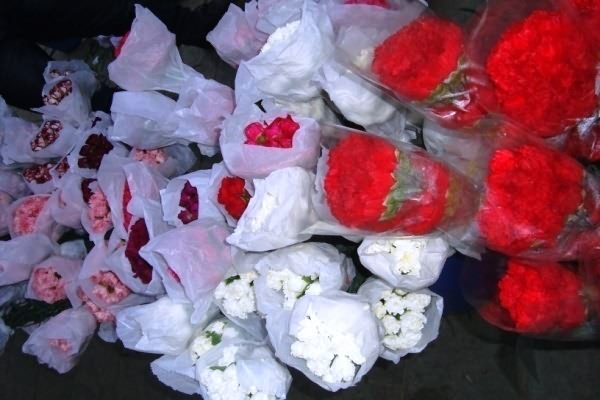


Packaging of Carnation Corrugated boxes packaging of Carnation
|
S. No. |
Box Size |
Stem length |
|||
|
|
40 cm |
50 cm |
60 cm |
80 cm |
|
|
1 |
100 x 40 x 20 cm |
700 Stems |
600 Stem |
500 Stem |
400 Stem |
|
2 |
100 x 40 x 21 cm |
700 Stems |
600 Stem |
500 Stem |
400 Stem |
5. Transport
Tempo, small trucks are used for transport of carnation cut flowers in domestic market.
3. Post Harvest Operation of Gerbera
1. Harvest
The flowers are kept is clean bucket after harvesting and send in the packing hall.
2. Grading
This is done according to the stem length of gerbera. The damaged, pest and disease infested stem should be rejected. Gerbera should be free of any developmental shortcomings, including growth cracks, irregularly shaped hearts and irregularly shaped flowers. Gerbera should be free of heels.
 Bull head bud of Gerbera
Bull head bud of Gerbera
3. Sorting
Gerbera cut flower is generally sorted on the basis of maturity and flower diameter.
4. Bunching
Individual gerbera flower bud is covered by a plastic packet closed at the sepals side and open towards petal side.
Large-bloomed gerbera bunches should consist of 10 stems and bunches of mini gerberas should have 20 stems each.
5. Packaging
- Gerberas must have been sufficiently pre-watered in clean water and then packed dry in boxes.
- Gerberas with stems of 35-40 cm should be packed in lined boxes, provided their minimum length is shown on the auction form and the box.
|
S.No. |
Box Dimensions |
Stem Length |
Stem per bunch |
Number of bunches per box |
Total Stems |
|
1 |
100 cm X 45 cm X 20 cm |
40 cm |
10 stems |
35 bunch |
350 stems |
|
2 |
100 cm X 45 cm X 21 cm |
40 cm |
10 stems |
35 bunch |
350 stems |
For domestic market 3 ply corrugated boxes are used for Gerbera cut flowers.
Export packaging
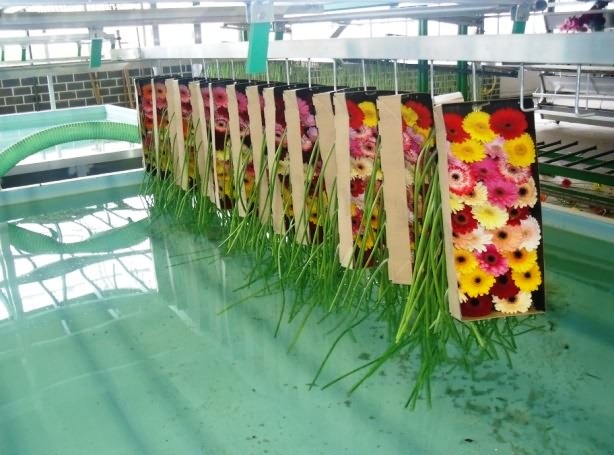
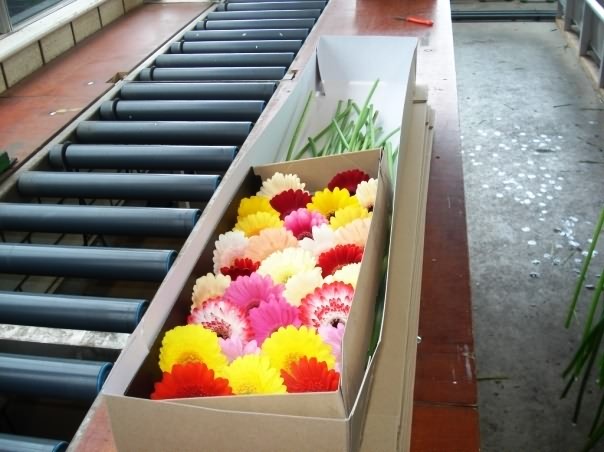


Dipping of gerbera stem in water Corrugated box on conveyer belt
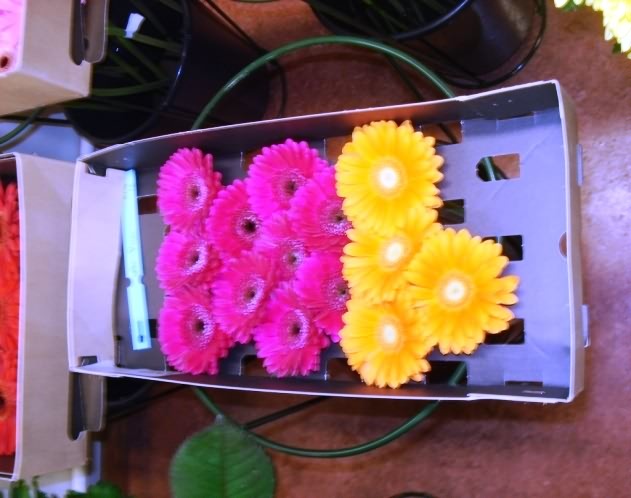


Drying of gerbera stems Corrugated boxes packaging of Gerbera
Domestic packaging
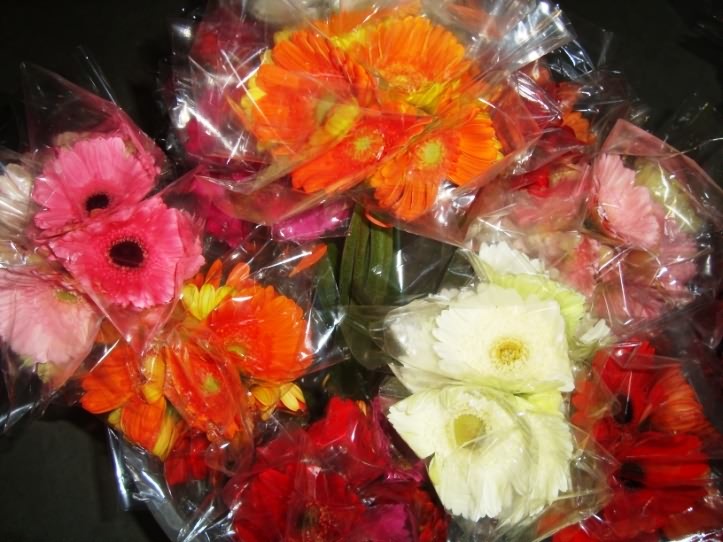
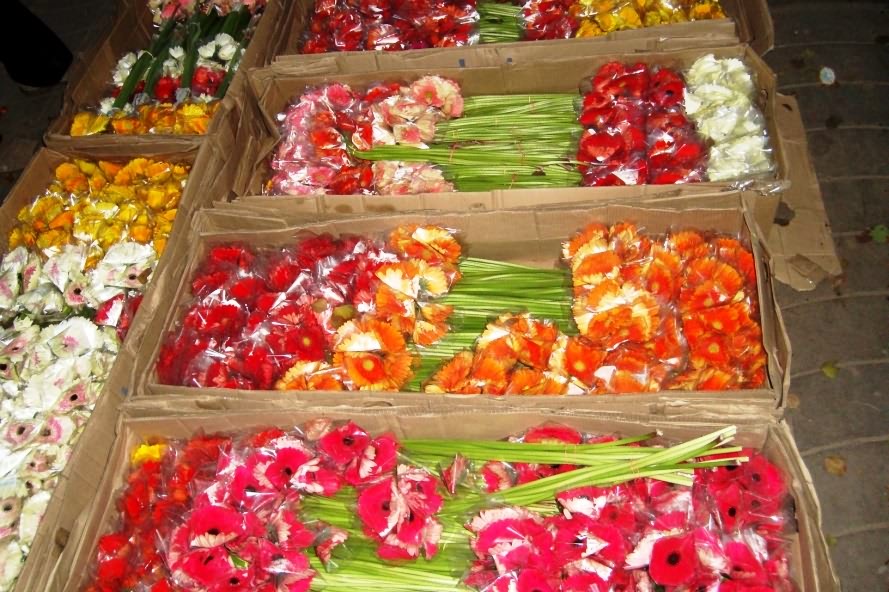


Gerbera in plastic sleeves Gerbera Flowers in boxes
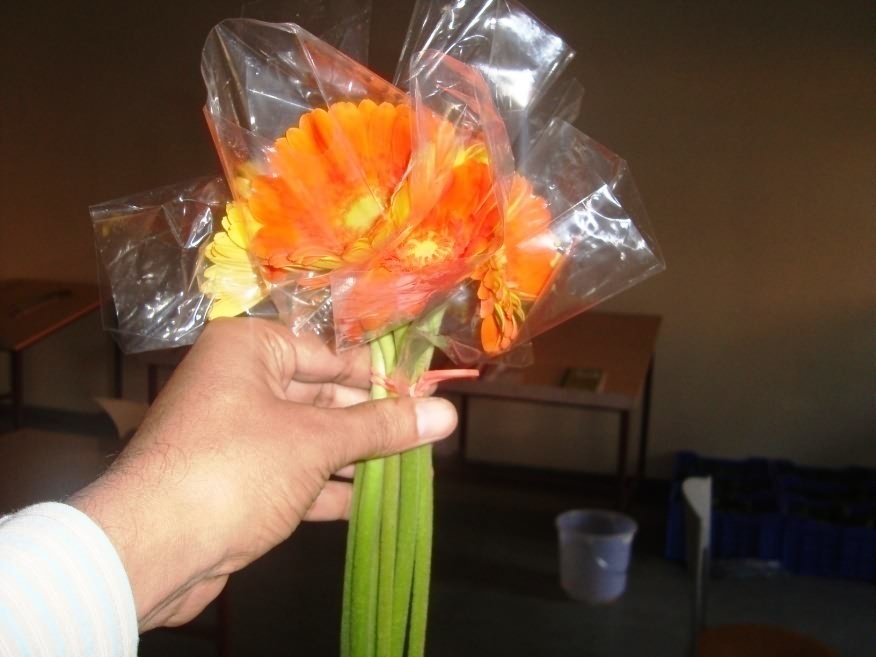

Gerbera flowers covered with polythene sleeves
6. Transportation
All the boxes should be stacked upside down (lids at the bottom) when they are loaded onto the trolley. They are transported to domestic market by tempo and railway, where as incase of export they are transported in refrigerated van to airport, then by air freight to destination.
Authors
Satya Narayan Choudhary
Trainer (Greenhouse specialist)
International Horticulture Innovation and Training Centre
Durgapura, Jaipur (Raj.)
Email: