गुलदाउदी रतुआ और उसका प्रबंधन
Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium) is a commercial ornamental crop grown for its beautiful flowers used either in garland making or in landscape. There are 200 species of Chrysanthemum grown around the world. Major chrysanthemum growing states in India are Karnataka, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Himachal Pradesh.
Chrysanthemum is affected by many pathogens viz. white rust, stem blight, wilt and crown gall. The rust disease is becoming serious problem of late.In this article rust diseases of chrysanthemum, their symptoms, epidemiology and management measures are discussed.
In chrysanthemum two different types of rust disease are observed. White rust is caused by Puccinia horiana & Brown rust is caused by Puccinia chrysanthemi.
The chrysanthemum white rust is treated as quarantine pest in many countries. The disease was first reported in Japan in 1985 and moved to England in the 1960s. This pathogen is native to East Asia and now widespread in Australia, Africa, Europe and South and Central America. It was first recorded in India in 2012 from Udhagamandalam in Tamil Nadu and Bengaluru in Karnataka.
Symptoms of rust in Chrysanthemum
White rust:
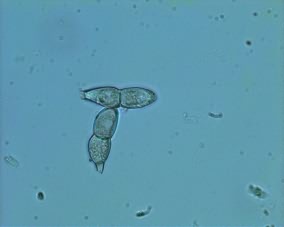
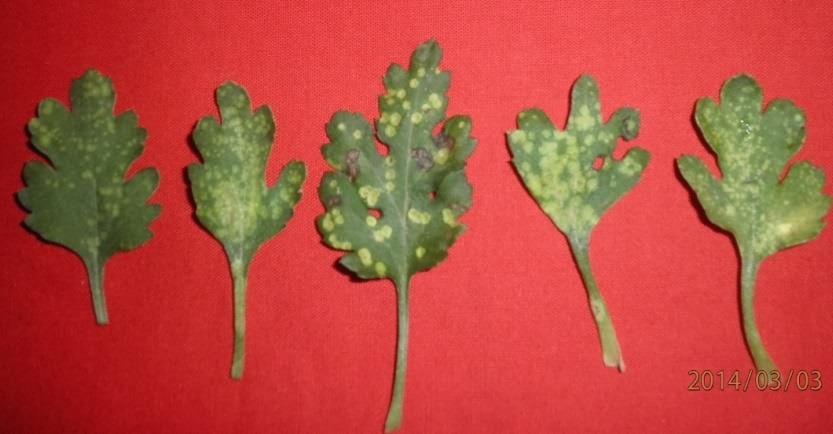
On the lower side of the leaves, cream or yellow pustules are formed which are minute in size in the beginning. Later the size of the pustules increases. When pustules mature, the centre portion turn pinkish which later on turns brown in colour. On the upper surface, there will be yellow spots that later turn necrotic. The pustules contain two celled teliospores. In severely affected crop the rust sori with pustules are seen on bracts and stems. Telia are mostly erupted on the leaf surface, sometimes sunken, compact, yellowish, white or yellowish white, rarely pinkish, 0.5-4 mm in diameter. In severely infected crops leaves wilt and dry up(any defoliation).
Brown rust:
Unlike the white rust, in this case small brown pustules appear on lower surface of the leaves with corresponding yellow lesions on the upper surface of the leaf. The spores represent the uredospores unlike teliospores in white rust. The rust spores are chocolate‑brown in colour.
|
Brown rust of chrysanthemum |
White rust of chrysanthemum |
|
|
 |
|
Brown pustules on the lower side of leaves |
White pustules on the lower side of the leaves |
 |
|
|
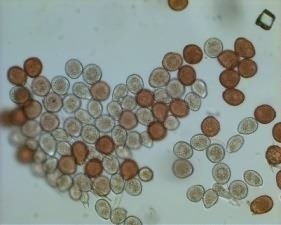
Uredospores of Puccinia chrysanthemi |
Teliospores of P. horiana |
Fig.1 Differences in the symptoms and spore morphology with respect to brown and white rust in chrysanthemum
Survival and spread
Chrysanthemum white rust is microcyclic rust. It survives on living chrysanthemum foliage. Teliosporesin the leaf pustules germinate to produce basidiospores that are airborne. The teliospores at very low night temperature i.e. below 17-19°C produce promycelium which in turn release the basidiospores.
The basidiospores are the infective spores while teliosporesdon’t infect chrysanthemum directly. Generally, the severity of occurrence of this disease coincides with the post-monsoon season followed by the winter spell (October to December). The disease spreads to new areas through infected planting material.Brown rust is spread by the airborne uridospores.
Management of rust in Chrysanthemum
- Use disease free planting material (Cuttings) from reputed source.
- Quarantine which means exclusion is the best strategy for the white rust. If white rust is found in new area, infected plants should be destroyed to prevent further spread.
- To manage white rust spray Chlorothalonil 75% WP at 0.2% as preventive measure and Propiconazole 25EC at 0.1% as curative.
- For the brown rust management give preventive spray with Chlorothalonil75% WP @ 2% followed by curative spray with Carboxin37.5%+ Thiram37.5%DS at 0.2 per cent.
- Cultural practices to maintain low humidity in field is important for both rust pathogens. Follow drip irrigation and recommended spacing. Avoid flood and sprinkler irrigation.
- When cropping period is over follow sanitation by burning of infected plant debris.
White rust is an emerging disease of chrysanthemum in India with restricted distribution.With the information provided, chrysanthemum growers can identify white rust in newer areas and take timely management interventions to prevent its further spread.
Authors:
Sriram S, Priti Sonavane and Sandeep Kumar G.M.
ICAR-Indian Institute of Horticultural Research,
Hessaraghatta lake post, Bengaluru-560 089
Email: