कारनेशन फूलों की संरक्षित खेती
Carnation is a half hardy perennial with branching stems and tumid joints. Leaf blades are simple, entire and usually narrow. Each stems form a terminal flower and hence inflorescence is generally a terminal cyme. The flowering shoots of carnation are marketed in two forms, standard form and spray or miniature form. Perpetual flowering and green house carnations are of modern origin.
 Botanical Name : Dianthus caryophyllus
Botanical Name : Dianthus caryophyllus
Family : Caryophyllacae
Native : Southern Europe
Temperature : Night 14ºC-16ºC, Day 17 ºC- 22 ºC
Crop duration : For Two years
Chromosome no. : 2n=30
At present enormous varieties are available with many attractive colours, remarkable ranges of shapes , sizes and delicate fragrance.
Types of carnation:
- Standard type: In Standard type, flowering buds formed on short lateral shoots arising from the axis of the upper leaves are removed to leave one large, terminal flower on a long leafy stem. It has one large flower on an individual stem.
- Spray type: In spray type, terminal flower bud is removed at an early stage to encourage more even development of the lateral flowers, which then produce a multiple flowered stem.
- Dianthine type :They are more or less similar to the spray varieties, but in this type flowers are smaller and produce more flowers on long stems. Market of these types of carnations is small.
- Mignon and Microtype : These types have much in common with the normal spray varieties. The stems, however are smaller and yield is higher than spray varieties. Demand for these types in the market is less.
Varieties of Carnation
| Colour | Varieties of Standard Type Carnation |
| Red | Aicardi, Barbarot, Balance, Corba, DomingoGaudina, Hilwarda, Kooij, Santamaria, Selecta, Turbo |
| Pink | Charmant Pink Dona, Famosa Pink Dover, Pink Shiva, Pink America, Pink Monterama |
| White | Angelica, Baltico,Hydra White Liberty, Madame Coletta, Viking |
| Yellow | Diana, Hermes, Salmanca ,Tobago,Yellow solar |
| Cream | Kamar, Sablia, Sagres, Shanteng |
| Cerine | Cherry Solar, Dona, Maxi, Rubes co, Shiva |
| Orange | Malaga, Nabita, Nova Scollia, Olymbia, Solar |
| Green | Green Elegance, Lady green ,Lenny,Nokia,Pradorova |
| Lidae | Farida , Remo |
| Fancy | Alibaba, Garuda, Rindez Sonya |
Varieties of Spray Type Carnation |
|
| Red | Etna , Karma, Rony, |
| Pink | Anne lies, Barbara, Silvery pink |
| Yellow | Alicetta, Lior ,Odeon |
| White | Excel, Royalette, Tibet |
| Others | Exquisite, Kissi , Scarlet Elegance |
| Micro | Carnation : Eolo, Pink Eolo, Wiko |
| Mini | Spray Carnation : Lima, Onia, Roland |
Growing region wise Varieties of carnation
| State/ Region | Cultivars |
| Maharashtra - Pune | Aristo, Flair, Fambo,Stylo, Scania,William Sim |
| H.P. -Solan | Arthur Sim, Candy, Espana, Pamir, White Candy |
| Punjab-Ludhiana | Arthur Sim,Sam’s Pride, Scarlet Elegance |
| T.N.-Kodaikanal | Arthur Sim, Scania, Scarlet, Elegance and Star light |
| W.B.-Kalimpong | Arthur Sim, Dusty,Scania |
Propagation of Carnation:
Planting Material of Carnation crop:
Success and failure of carnation crop depends upon the selection of cuttings for planting. The selection and production of high quality carnation cuttings requires high degree of specialization. The stem tip cuttings must be of good diameter and have closely spaced leaves. The cuttings must be taken at the stage of vegetative growth.
The stock plant must be pinched and cuttings should be harvested regularly, when the shoots are long enough to make cuttings. Top of the plant is removed leaving 5 to 6 paired leaves on the plant.
For spray type, length of cutting should be 7 to 10 cm, while in case of standard type, 10 to 15cm long cuttings are preferred, cuttings roots in 2 – 3 weeks, if they are placed in favorable environment.
Treating the cut ends with 2000 ppm IBA, encourages more roots. Misting water in the propagation units helps in better rooting.
Soil for carnation crop:
Red sandy loam soil with good drainage is best for the cultivation of carnation, land polyhead up to 80 – 100 cm deep. Optimum soil pH is 6.5 addition of calcium carbonate or dolomite , lime stone corrects acid condition and also supplies calcium and magnesium for plant nutrition. Addition of sulphur or acid forming fertilizers will reduce the soil pH if it is on the higher side. EC of 1.2 at the start and 1.5 at the generative period is ideal.
Soil Sterilization:
Formaldehyde :
- Mix with water in 1:10 proportion and drench the beds
- Cover the beds with polythene for 7 days
- Stir the soil to evaporate the chemical
- Leach the soil with water to remove the chemical
- Planting has to be done after 2 weeks
Dazomet (Also known as Basamid granules):
- Micro granuler soil fumigent contains 98% Dazomet
- When mixed with soil, releases biologically active gases like methyl isocyanate, which penetrates between soil particles
- It leaves no harmful residues Dosage 40 gm/ sq.mt.
Application of Manures in carnation crop:
Well decomposed cattle manure - 25 kg/ sq. mt. ,
Leaf mould - 25 kg/ sq. mt. ,
Neem cake - 500 gm/ sq. mt.,
Bone meal - 200 gm/ sq. mt.,
Ideal pH - 6.0 – 6.8
Bed Preparation for Carnation crop: 
- Bed preparation for carnation crop is to be done after soil sterilization and proper washing out with water, when the field capacity of soil is reached.
- The beds should be prepared in the direction of gutters of the green houses.
- Leave sufficient space for main pathway, which is required for various operations.
- The green house columns generally should be on the beds.
- After preparation of beds avoid walking on the beds, which may damage the soil and bed structure.
- The paths in between two beds should be sufficiently wide to carryout all cultural operations, efficiently.
- In case of crops, where in support structures are required, the support structures are to be erected before final preparation of beds.
- After fumigation, the raised beds of given dimensions are prepared, like bed top width – 90 cm, bottom width – 100 cm, path width– 50 cm and height of bed – 30 cm.
Basal fertilizers application in carnation:
- Super phosphate – 200 gm/sq.mt.
- Muriate of potash – 150 gm/sq.mt.
- Magnesium sulphate – 50 gm/sq.mt.
- Borax – 2 gm/sq.mt.
Throughly mix with the soil and water plant after 2 weeks
Plant Spacing and Plant Density:
15 x 15 cm, 20 plants/ sq.mt [10000 plants/ 500 sq.mt.] usually 32 plants/ net m2 [per m2 of bed] and about 20 plants per gross m2 [per m2 of green house] are planted. This should be followed very strictly. Because more plants/ sq.m will just give a higher in the first flush, after wards this advantage disappears and more problems with disease will occur.
Before planting, place 7.5 x 7.5 cm supporting net on the beds. Plant the rooted cuttings as shallow as possible. Do not press the soil, because it may cause fusarium rot disease, which leads to the mortality of plants. Immediately after planting, drench with 1 g carbendazim or captan per lit of water. Continuous spraying of water should be given to maintain the soil wetness (i.e. minimum 10 days) to enhance the rooting of plants.
Fertigation (500 sq.mt. Area):
| S.No. | Name of fertilizers | Quantity (gm) | ||
A – Tank |
||||
| 1 | Calcium Nitrate | 600 | ||
| 2 | Potassium nitrate | 250 | ||
| 3 | FC EDTA/Sulphate(Three weeks after planting) | 15 | ||
| B – Tank (Tuesday, Thursday, Saturday) | ||||
| 4. | Mono ammonium phosphate 12:61:0 | 150 g | ||
| 5. | Sulphate of potash 0 : 0 : 50 | 800 g | ||
| 6. | Magnesuim sulphate | 600 g | ||
| 7. | Manganese sulphate | 5 g | ||
| 8. | Zinc sulphate | 3 g | ||
| 9. | Copper (copper sulphate) | 3 g | ||
| 10. | Molybdenum (Sodium molybdate) | 1 g | ||
| 11. | Boron (Borax) | 5 g | ||
(Sunday plain irrigation water)
Irrigation in Carnation Crop:
Over watering and poor drainage cause root death and stunted growth. Water logging would cause deprival of oxygen to plants. The growing medium should be evenly moist.
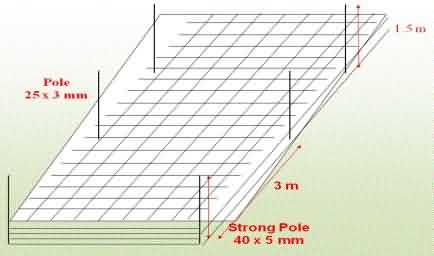 Crop Support (Netting):
Crop Support (Netting):
To ensure straight stems, the carnation crop needs to be supported with 4 (or) 5 layers of support material. Good support material is metal wire with a mesh width of 7.5 x 7.5 cm to 15 x 15 cm minimum at every 3 mts, The wires should be supported with poles. The poles at the beginning and the end of each bed should be strong enough and be in cast concrete.
For an optimal support of the crop, an increasingly width of meshes may be used. (e.g.) Bottom net of 7.5 x 7.5 cm, 2nd net of 12.5 x 12.5 cm, Upper nets of 15 x 15 cm
Pinching of Carnation:
Pinching is an important operation in the successful production of quality carnation. There are generally two types of pinching used.
(i) Single pinch : This method facilitates more rapid flowering but all stems flower at same time. After the establishment of plants, about 3 – 4 weeks after planting, the apex shoot is pinched leaving on the 5th – 6th pair of leaf or leaving 5 – 6 lateral shoots to develop.
(ii) Pinch and half method : After initial pinch, one half of the breaks from the first pinch are pinched a second time about three to five weeks after first pinch.

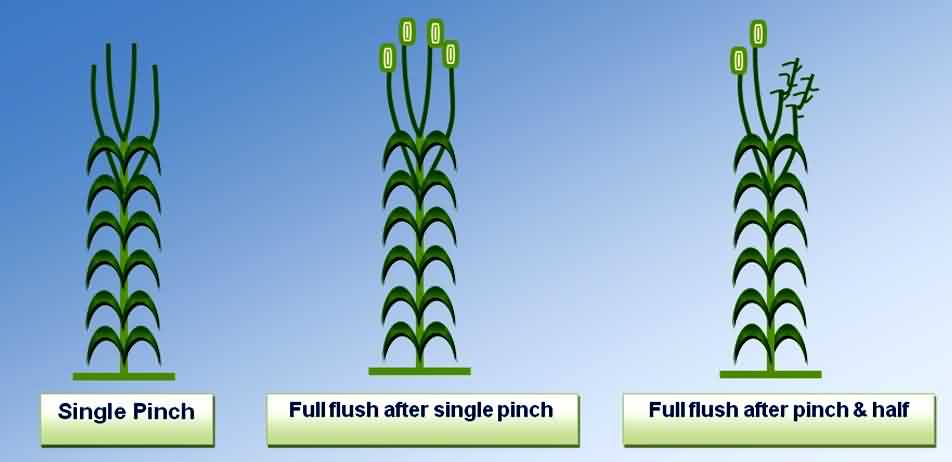
This method result in lower yields in first flush compared to single pinch method, it will result in more even and stable production over time follows pinching with spray of fungicides.
 Disbudding in Carnation:
Disbudding in Carnation:
The practice of removing undesirable immature flower buds other than central terminal bud is called disbudding. But in case of spray carnations only the central terminal bud is removed to encourage lateral flower buds to develop care must be taken to avoid any injury to the main stem.
De Shooting in Carnation:
It is found to influence flowering in carnation. Removal of all secondary shoots from 5 weeks after planting and on alternate days till flowering does not affect the stem lengths but stem size and flower size is increased by 10 to 15 %.
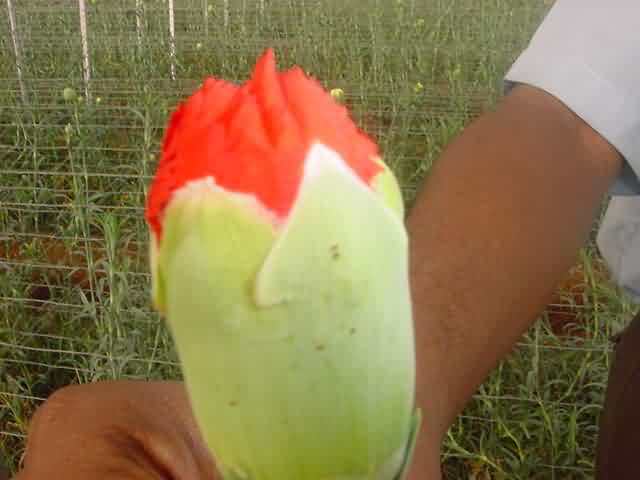
Pests of Carnation:
Red Spider Mites:
Symptoms :
- These have the ability to produce fine silk webbing, spider mites are very tiny and very small and are difficult to identify.
- They suck sap from the leaves which results in tiny yellow (or) white speckles. Once the foliage of a plant becomes bronze it often drops prematurely. Heavily infested plant may be discoloured stunted.
- Favourable condition
- High temperature and low relative humidity
- More populated crop (dense crop)



Control measures
- Apply Thiovat (Wettable sulphur) @ 2.0 gm/lit , Metasystox (Oxy-demeton-methyl) @ 1.0 ml/lit or Vertimec (Abamectin) @ 0.4 ml/lit of H2O.
Aphids of Carnation:
Symptoms:
- These are the sucking insects. Feeding usually occurs on buds and undersides of leaves. Feeding on young leaves results in distorted leaves as they continue to grow. Older leaves may display patches of chlorolic spots. Nymphs and adults suck the sap from the leaves, stems and flower buds in colonies. Aphids excrete honey dew, which results in black fungus development on plants.
- Favourable conditions:
- Cloudy weather favours rapid build up of aphids population
- Low temperature favours development of young aphids
Control : Apply Asatap (Acephate) @ 0.5 – 1.0 gm/lit of H2O
Thrips of Carnation:
Symptoms:
- Both the nymphs and adults suck the sap from leaves and flower. They excrete brown droplets, which afterwards true black. Leaves may fade and shrivel in case of heavy infestation and foliage becomes silvery.
- Favourable condition
- Mainly temperature affects the thrips population
Control
- Spray Asatap (Acephate) @ 1.0 gm/1 lit of water (as Decis (Deltamethrin) @ 0.5 ml/lit of H2O (or) Exodust @ 1.0 gm/lit of H2O.
 Caterpillars in Carnation Crop:
Caterpillars in Carnation Crop:
Symptoms:
- Caterpillars feed on the leaves. Sometimes they may bore into the buds plant growth is affected adversely
- Favourable condition
- Affected by caterpillars, Infected bud
- Warmer climate in polyhouse
- Fluctuation of relative humidity in the polyhouse
- Fluctuation of temperature in the polyhouse
Control :
- Spray Monocrotophos (Monocil) @ 1.0 ml/lit of H2O (or) Polytrin (Cypermethrin) @ 0.5 ml/lit of H2O.
Nematodes problem in Carnation cultivation:
- Root knot nematode is a serious pest. Infected plants usually appear stunted and tend to wilt on warmer days.
- When such plants are dug, the root galls are generally conspicuous and easily identified.
Control : Apply Thionet (Phorate) @ 6.0 gm/sq.mt/Basamid (Dasomet) @ 6.0 gm/sq.mt.
Diseases of Carnation crop:
Powdery mildew :
- On the top of the leaves white, powdery fungal growth develops consisting of hyphal threads and spore carriers. The fungus is also observed on the underside of leaves. Malformation of young leaves takes place due to infection of powdery mildew. Brown spots develop on full grown leaves.
Control:
- Spray Roko (Thiophinate methyl) @ 2.0 gm/lit or Bayer (Biternol) @ 2.0 gm/lit of H2O
 Black spot (Alternaria dianthi):
Black spot (Alternaria dianthi):
The disease is characterized by appearance of round purplish spots on the leaves, enlarging slowly with brownish black centre having sporulation. The leaf tissues surrounding this spot turn yellow, severe infection leads to premature death of the leaves.
Control:
spray Chlorothalonil @ 1.5 gm/lit of H2O.
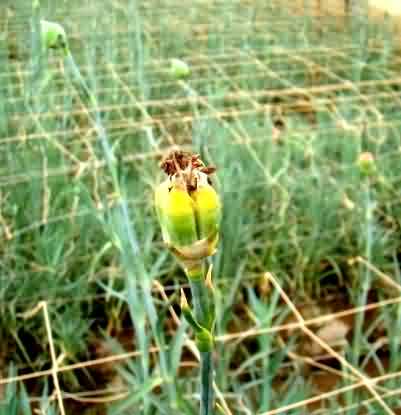 Botrytis in carnaton crop:
Botrytis in carnaton crop:
Symptoms:
The fungus is usually identified by the development of fuzzy, grayish spore over the surface of the rotted tissues. The fungus causes a brown rotting and blighting of affected tissues. Blooms are worst affected resulting in poor quality.
Control:
- Spray Carbendazim / Capton @ 2 g / litre of water.
 Phytophthora [Foot rot] of Carnation crop:
Phytophthora [Foot rot] of Carnation crop:
Symptoms:
Withering and yellowing of foliage, leaf death external browning of stems and internal browning at nods appear. Stem and root rot may take place. Lower leaves become purple and dry shortening and blackening of stems take place and rotting of stems can be observed.
Control:
- Apply Alleite @ 1.5 gm/lit of H2O (as Kavach (Chlorothalonil) @ 1.5 gm/lit of H2O.
Pythium [Root rot] of Carnation crop:
Symptoms:
Its infection results in stunted growth and ultimately drying of entire plant.
Control:
- Spray Bavistin (Carbendazim) 2.0 gm/lit or Alleite @ 1.5 gm/lit or as Kavach (Chlorothalonil) @ 1.5 gm/lit of H2O.
Symptoms:
- Infection takes place through wound. The lower leaves start becoming yellow followed by withering of leaf bases and yellowing of mid ribs and eventually the branch wilts. Brown discoloration and shredding of vascular bundles.
Control:
- Spray Alleite @ 1.5 gm / lit or Kavach (Chlorothalonil) @ 1.5 gm / lit of H2O.
Physiological Disorders in Carnation crop:
It is a major problem in carnation. This is due to fluctuation in temp. (< 10º C ), moisture situation, low N, high ammonical N, boron deficiency and varietal character.
Control:
- This may be rectified by uniform watering, Higher nitrate to ammonical N ratio fertilizer applications, spraying of borax and avoid planting of varieties which are prone to split. e.g. Carbet, Espana ,Pamir. Use small ruber band on bud when it show opening.
Sleepiness:
Carnation petals cup upwards and do not open. This is due to ethylene gas emitted by fruits and vegetables. This is controlled by not mixing the flowers with vegetables and fruits during storage and transit. Keep ethylene absorbant tablet like purfil pad.
 Weak Stem:
Weak Stem:
Common during winter months due to reduced light & Excess Nitrogen
Boron Deficiency:
Symptoms:
Malformed flower buds, short stems and excessive branching.
Control:
- To rectify the apply boron through drip irrigation @ 30 gm borax / 10 sq.mt. once in a year
Harvesting of Carnation crop:
- Harvesting of carnation starts from the end of the fifth month in some varieties and starting of the sixth month in other varieties.
- The flowers should be harvested early in the morning or late in the afternoon.
- The flower must be placed in buckets with clean water or 1ml of sodium hypochlorite (15% a.i.) in 10 litter of water.
Carnation is harvested in three stages of harvests, namely
Tight bud stage :- Advised for long distance market but in this flowers may not open sometimes
Paint brush stage :- Standard carnations should be harvested when the outer petal unfold nearly perpendicular to the stem. Spray types are harvested when two flowers are open and the bud shows colour,
Semi open stage :- Ideal for short distance marketing.
Grading of Carnation Cut flower:
|
Code |
Stem Length (cm) |
|
|
40 |
40-50 |
|
|
50 |
50-60 |
|
|
60 |
60-70 |
Pulsing of Carnation:
Solan centre
- 1mM STS + 10% Sucrose for 8hrs.
- 30 mg / L Silver Nitrate + 4% Sucrose
- 30 – 300 mg / L 8-HQC + 4% Sucrose
- 30 – 300 mg / L Copper Nitrate +3 % sucrose
- 50 mg/ L Benzalkone + 10 % Sucrose
Commercially used Floral Preservatives
Chrysal, AVB, Florissant 100 and Forever.
Doses : @ 2ml of Chrysal / Florissant 100 in 10 L water.
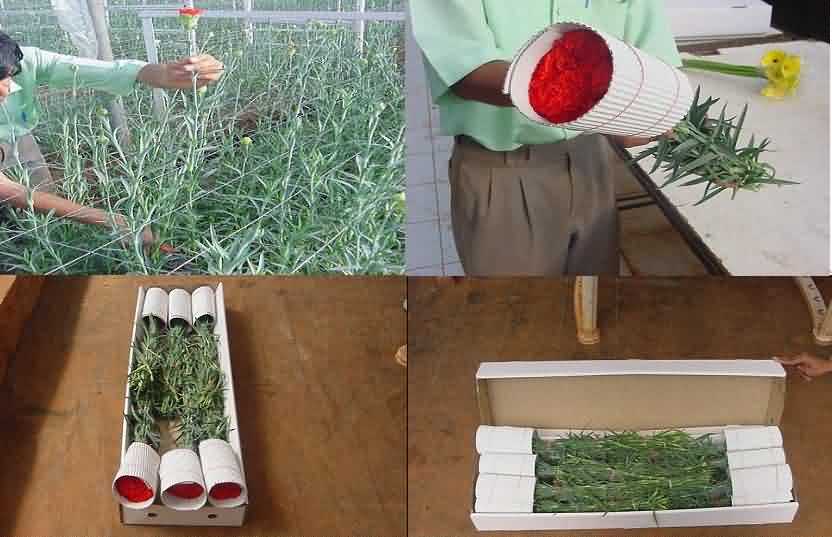
Packaging of Carnation:
Wrapping the cut carnation flower in c.sheet , putting rubber band and packing in fibre board boxes
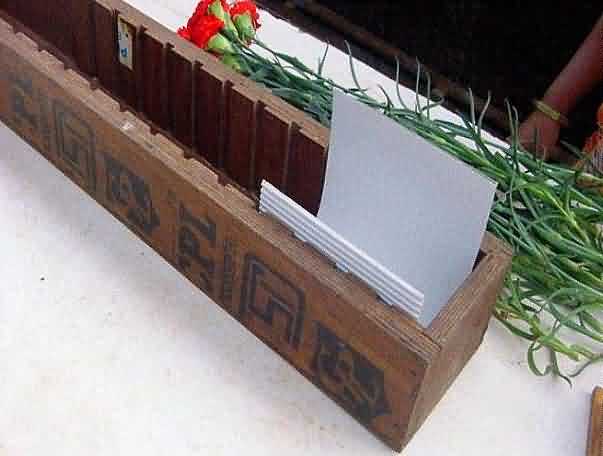
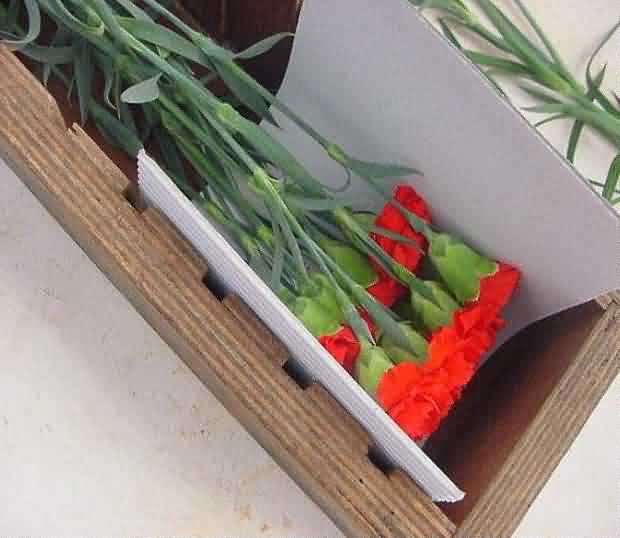
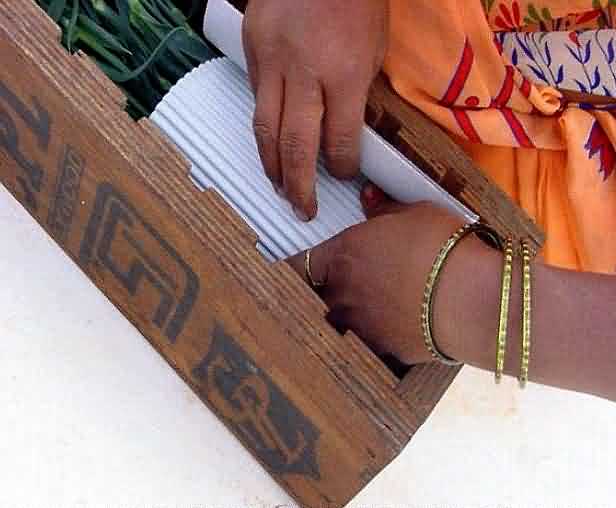
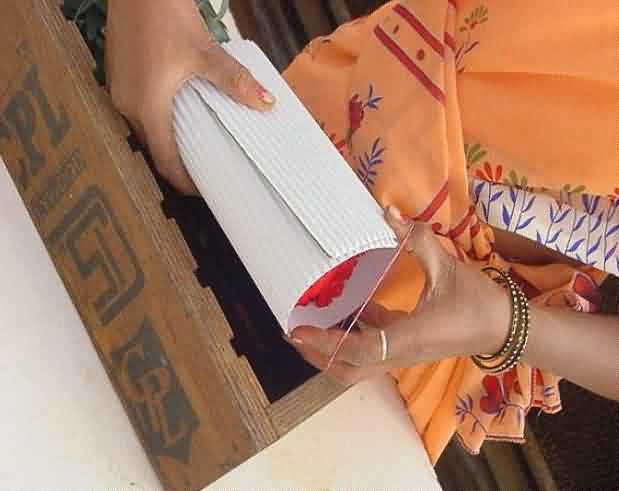




wrapping the cut carnation Putting rubber band on w.cut carnation
Packaging sizes:
Flowers are packed in bunches and sleeved in plastic sheets or newspaper as desired by customer. The sleeved bunches are packed in cardboard boxes having 122 cm L x 50 cm W x 30 cm H that are brought into the cold store and cooled down
Post harvest handling:
Storage - The cut ends of the flower stems are dipped for 10 minutes in 1000 ppm STS and there after pulsed at 10 to 20º C temperature for one hours in 5% sucrose + 150 ppm HQC (Hydroxy Quinine citrate). Cut carnation at paint brush stage, can be stored under refrigerated for 3 weeks at 4± 1ºC, both under wet and dry storage condition at Ludhiana.
Vase life - 14 to 21 days preservative solutions are 4% sucrose + 30 ppm AgNo3, 4% sucrose + 300 ppm 8 HQC.

Yield of Carnation crop:
Standard type: 200 Flowers per square meter
Spray type: 250 Flowers per square meter
Author:
Satya Narayan Choudhary
Asstt. Trainer,
International Horticulture Innovation and Training Centre,
Durgapura- Jaipur
Email: