कीट प्रबंधन में जैव कीटनाशकों की भूमिका
More and more quantities of chemicals are used for agriculture intensification to feed on ever growing population. In fact the pest induced loss is on the rise despite increasing usage of pesticide, fortunately, realizing of the negative effect of these chemicals on natural and natural resources like pollution. Pesticide residue, pesticide resistance etc, have forced many to shift focus on to more reliable, Sustainable and environment friendly agents of pest control, the bio pesticides. In view of this demand and Governments efforts to mitigate climate change, biopesticides are going to play an important role in future pest management programme.
Biopesticide :-
Bio pesticides include " naturally occurring substance that control pest (biochemical pesticides), microorganism that control pest (microbial pesticide) and pesticidal substances produced by plants containing added genetic materials (Plant-in corporate protectants)
Biopesticides are biochemical pesticides that are naturally occurring substance that control pest by non toxic mechanism.
Biopesticides are natural plant products belonging to the secondary metabolites include alkaloids, terpenoids, phenolics etc.
Potential of Biopesticides in IPM :-
Biopesticides fall into three major classes :
- Microbial pesticide, Which consist of bacteria, entomopathogenic fungi and viruses. Entomopathogenic nematodes are also often classed as microbial pesticides, even though they are multi cellular.
- Plant Incorporated Protectants (PIPs), which have genetic material from other species incorporated into their genetic material (i.e. G.M.crops)
- Biochemical pesticides, which are naturally occurring substances that control pest by non toxic mechanisms.
Biopesticides, key component of IPM programme, are highly specific affecting only the targeted pest or closely related pest and do not harm humans or beneficial organisms while chemical pesticides are broad spectrum and known to affect non-target organism including predators and parasites as well as humans.
Use of bio pesticides as a component of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme can greatly decrease the use of conventional (chemical) pesticides, while achieving almost the same level of crop yield.
Utilization of Bio Pesticide and Bio Control Agent in Agriculture:-
Increasing environmental regulatory and market pressure, along with increasing pest resistance are dictating a progressive move away from chemicals for insect pest control. Insect pathogens (virus, bacteria, fungi and nematodes) produced artificially and formulated into microbial biopesticides, can provide best alternatives to chemicals
Insect pathogens constitute a group of potentially valuable IPM tools which are selective and generally safe to the environment.
Microbial biopesticides are insect pathogens which have been produced artificially and formulated for application to crops.
Microbial pesticides have varying mode of action. Bacteria and viruses must be consumed to take effect, while fungi and nematode can enter the insect via the cuticle (skin). Bacillus thuringiensis, a bacterial diseases of Lepidoptera, Coleoptera and Diptera, is a well known insecticide example, because it has little effect on other organism, it is considered more environment friendly than synthetic pesticide. The toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt toxin) has been incorporated directly into plants through the use of genetic engineering.
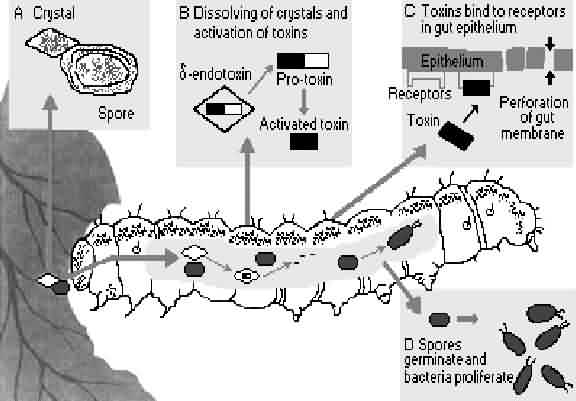
Mode of Action Bt
Other microbial control agents include products based on :
- Entomopathogenic fungi (eg. Beauveria bassiana, Lecanicillium Spp., Metarhizium Spp.)
- Plant diseases control agents include Trichoderma Spp. and Bacillus subtilis also used to control plant pathogen.
- Beneficial nematodes attacking insect (eg. Steinernema feltiae) or slug pests.
- Entomopathogenic viruses.
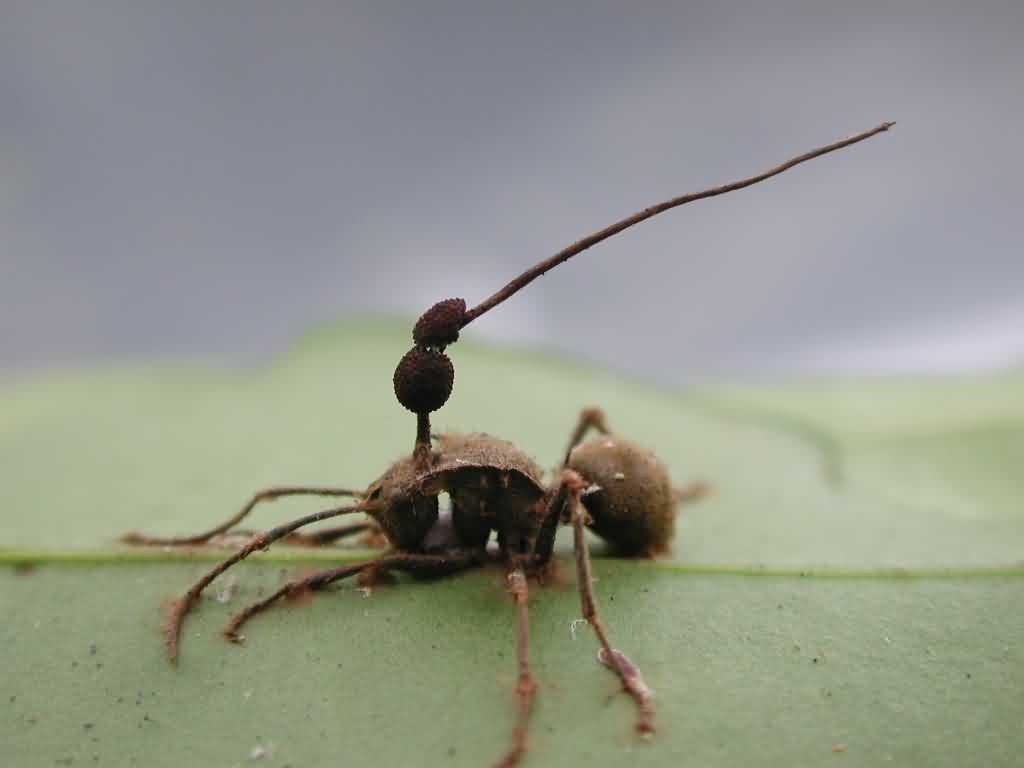


Entomopathogenic viruses Entomopathogenic fungi
Some Success Examples of Bio-pesticide and Bio-Control in IPM :-
- Control of diamond back moth by Bacillus thuringiensis.
- Control of Mango hopper, Mealy bugs and Coffee pod borer by Beauveria.
- Control of White fly on cotton through Neem products.
- Control of Helicoverpa on chickpea by NPV
- Control of Sugarcane borer by Trichogramma.
Factor affecting growth of Biopesticides. :-
However, some of the factors which have restricted the growth of biopesticides are :-
- Law reliability because of low stability in effect.
- Target specificity which distracts farmers.
- Slow in action compared to synthetics.
- Shorter shelf life.
- Erractic availability of biopesticides in the market.
- Alredy established and strong market of chemical pesticides.
- Regulatry system favorable to chemical pesticides and the gradual disappearance of multiple or mixed cropping, which known to keep away the magic bullet chemical pesticide.
Aurthor
Rashmi Gauraha & Dr. Deepak Gauraha
RAEO, O/o Deputy Director of Agriculture, Raipur
E-mail:
