बेर में फल छेदक के खतरे का प्रबंधन ।
Ber is an important fruit crop grown under arid and semi-arid region of Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab, Gujarat, and other parts of India. Tree is well adapted to adverse climatic conditions, salinity and it gives good returns to the farmers. However, the avoidable loss is more due to insect pests and diseases.
Of the various insect pests infesting ber in India, borers are notorious as they are causing the direct damage to fruits and they are as follows
- Fruit flies, Carpomyia vesuviana Costa, Daccus correctus (Bezzi) and Dacus dorsalis (Saundars)
- Fruit/ Stone weevil, Aubeus himalayanus Voss
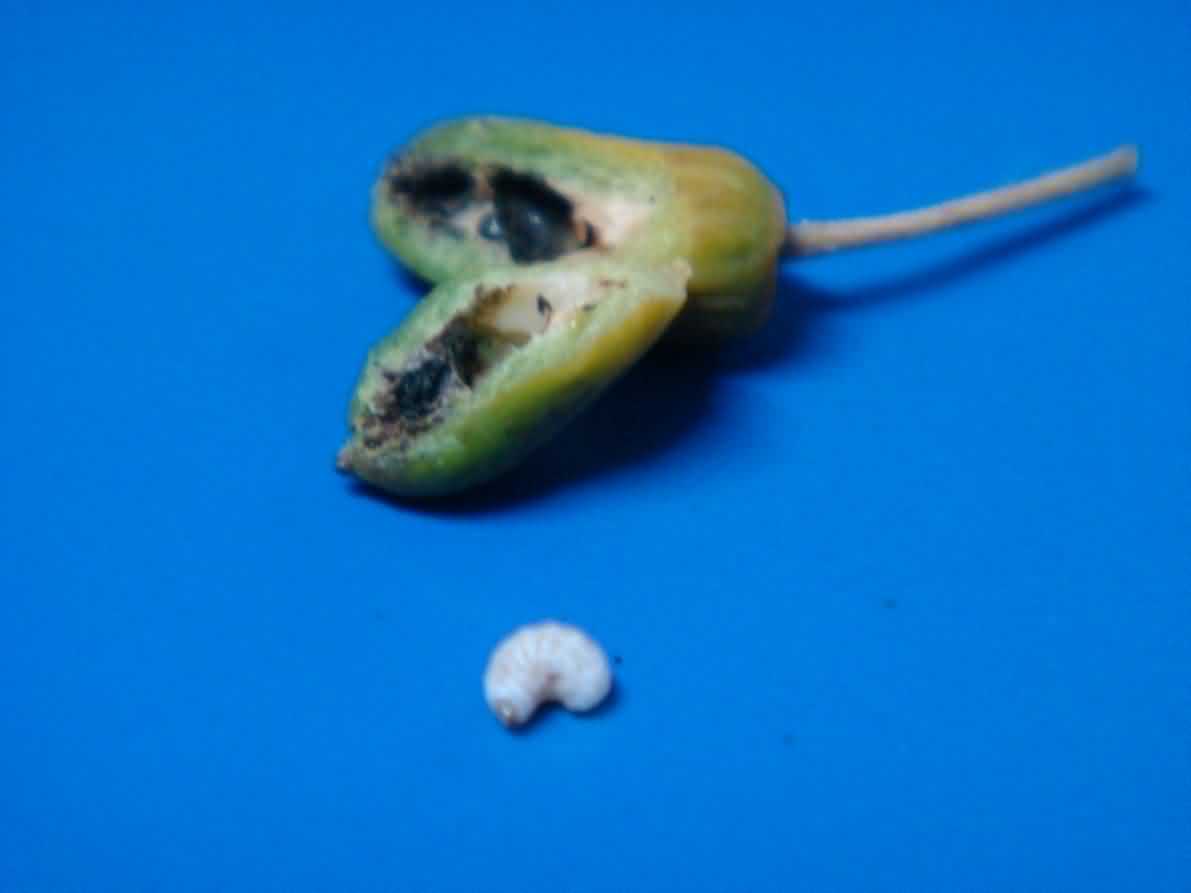
- Fruit borer, Meridarchis scyrodes Meyr
Presently, synthetic chemicals are widely used by the farmers to control theses pests. Sole reliance on insecticide will not give satisfactory control and it is essential to explore preventive measures to manage these pests. In this context, the integrated management strategy would be effective. Here, we are discussing some of the important tools IPM which can be employed for successful management of these pests.
|
Pest |
Nature of Damage |
Seasonality |
|
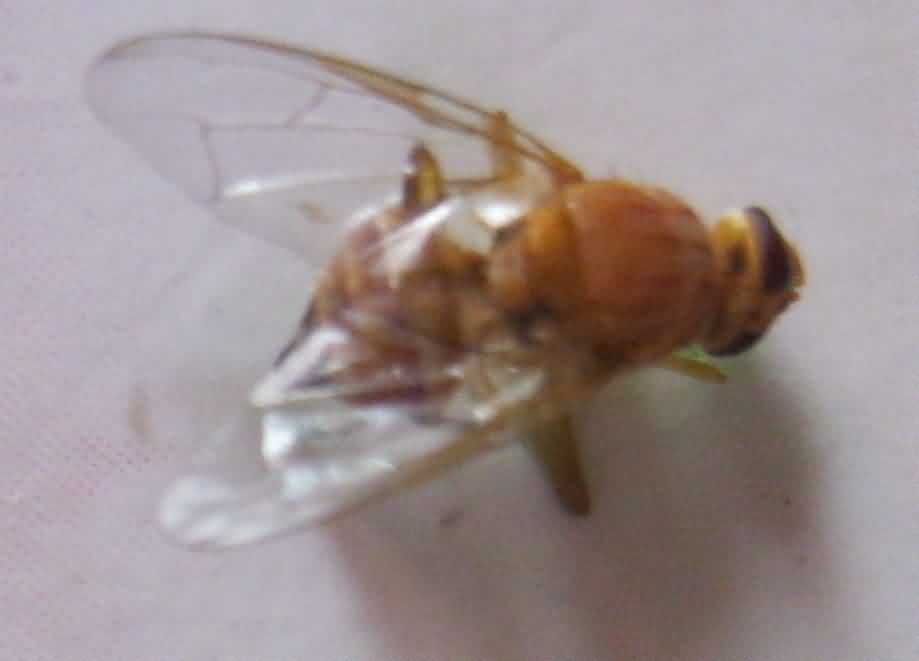
Fruit flies Carpomyia vesuviana Costa, Daccus correctus (Bezzi) and Dacus dorsalis (Saundars) (Tephrididae: Diptera)
Adult fly
Fruit fly infested fuit with undulated shape |
|
November to February |
|
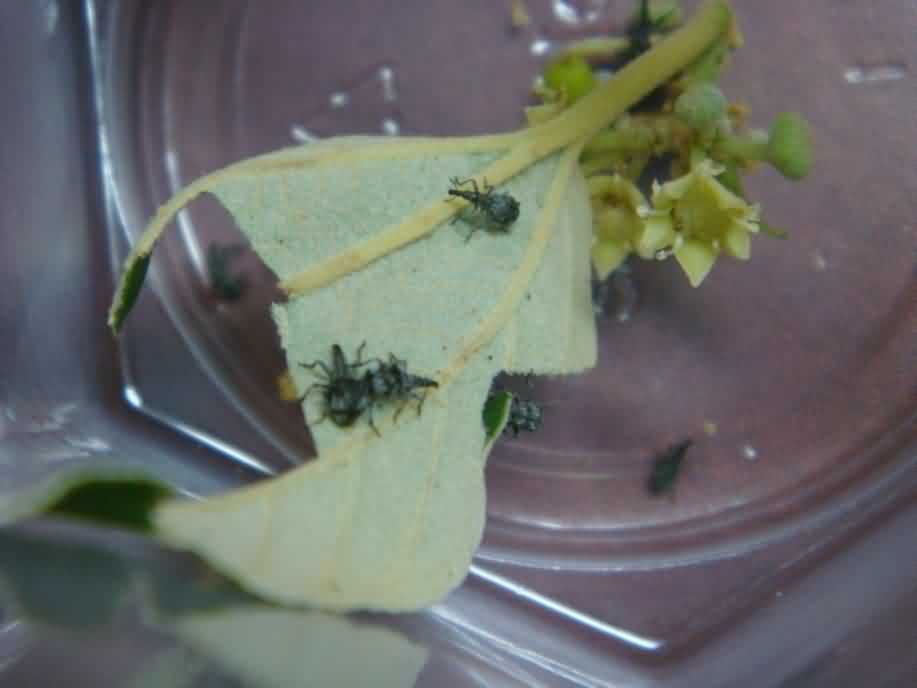
Fruit/ Stone weevil, Aubeus himalayanus Voss (Curculionidae: Coleoptera)
Damaged fruit and grub Adult weevils |
|
October to February |
|
Fruit borer Meridarchis scyrodes Myer (Lepidoptera: Carposinidae) |
|
November to December |
Integrated management strategies
Fruit flies
- Field sanitation to break the reproduction cycle.
- Destruction of wild ber bushes around the orchard.
- Summer ploughing to kill the residual pupae.
- Collection and destruction of infested and bird damaged fruits.
- Cultivars Umran, Mundia, Banarasi Kadaka, Tikidi, Dodhia, Meharun, Illachi and Chhuhara found to be promising against C. vesuviana.
- Foliar application of NSKE 5% followed by acephate 0.07% and repeat the NSKE 5% as a third spray at 15 days interval.
- Spray dimethoate 0.03%. In spray fluids add 0.5% jaggery. Use of fishmeal trap, 5mg of wet fish meal+ 1ml of dichlorvos with cotton when the infestation is severe.
- Use traps containing 1 ml methyl eugenol and 2 ml malathion/ litre of water and placing 100 ml of this mixture per trap at 10 traps per hectare would be effective against fruitfly D. correctus and D.dorsalis.
Fruit weevil/Stoneweevil
- Collection and destruction of infested fruits around the trees.
- Manual collection and destruction of adult weevil during morning and evening hours especially in the month of September and October will reduce the population.
- Spraying of Carbaryl 50 WDP at 0.1% just before the fruit setting and repeat the sprays at three weeks interval was found as effective.
Fruit borer
- Removal of wild ber trees present around or near to the ber orchard.
- Collection and destruction of all fallen fruits.
- Harvest of fruits at early stage when they are still green but fully mature.
- Spray schedule comprises of malathion at 2 ml or fenvalerate at 0.5 ml or carbaryl at 4 g /lit of water or Neem Seed Kernal Extract (NSKE) 5%; first spray at marble stage, second spray at 15 days later and third spray at fruit ripening stage, by alternate use of insecticides would be effective against the fruit borer.
Author:
V. Karuppaiah
Scientist (Agricultural Entomology)
Central Institute for Arid Horticulture Bikaner, Rajasthan
Email: