उत्तक संवर्धित केला - बढ़ाये कृषक की आय
Bananas are the fruits which now considered as world's 4th dietary staple after rice, wheat and corn. A number of people consume them in one way or the other. Banana (Musa spp.) comes under Musaceae family which have several species cultivated all round the world ( Musa acuminata, Musa balbisiana and Musa × paradisiaca for the hybrid Musa acuminata × M. balbisiana).
 It is world's largest herb and it is not a tree. The fruit type of banana is berry. A typical banana plant has 8 to 30 torpedo-shaped leaves that are up to 12 feet long and 2 feet wide. It is loaded with a number of vitamins and minerals viz., vitamin A, B, C and G.
It is world's largest herb and it is not a tree. The fruit type of banana is berry. A typical banana plant has 8 to 30 torpedo-shaped leaves that are up to 12 feet long and 2 feet wide. It is loaded with a number of vitamins and minerals viz., vitamin A, B, C and G.
It also contains alkali-forming minerals, potassium, natural sugars, protein and some fat. Bananas contain potassium-40, a radioactive isotope. They are easy to digest and provide quick energy and provide potassium lost during exercise.
They are the first choice of many professional athletes when they are competing. Banana is an edible fruit which is majorly grown in sub-tropical and warm climatic conditions. It is majorly grown in subtropical areas. They are grown in over 100 countries.
India ranks number 1 in the world’s highest Banana producing country. Ecuador is the world's largest exporter of banana. The best soil type for its cultivation should be alluvial which doesn’t retain water.
Various varieties grown in India are Dwarf Cavendish, Poovan, Grand naine, Ardhapuri, Basarai, Rasthali, Karthali and Karpurvalli. Banana is a crop that is conventionally propagated by vegetative means but there are several constraints in normal cultivation of banana which require to be addressed to meet the market demands.
Uses of bananas :-
- Bananas are eaten raw, dried or cooked in a variety of ways. It is used not only as fruit but also as vegetables and for making chips and other desserts.
- Unripened bananas are dried and ground into flour as they are rich in starch and used in bread and baby foods.
- It is extremely beneficial for hair, skin and eyes.
- It has weight loss promoting activities, increase bone strength, boosts the stamina.
- It is extremely beneficial for expectant mothers and increases the energy levels.
- Flowers of banana are also used in curries as vegetables and for snacks preparation in some parts of India.
- The leaves of bananas are also used as umbrellas, clothing, mats and roofing.
- In tropical countries banana leaves are also used to wrap foods. The fiber of the plant can be wound into twine.
Problems in conventional banana farming :-
The traditional banana farming encountered various problems listed below :-
- Natural regeneration of cultivated bananas through suckers is very slow due to hormone mediated apical dominance of the mother plant.
- A plant produces only 5-20 suckers during its life time of 12-14 months. For accelerating the propagation rate, suckers with growing buds or cut rhizomes called ‘bits’ and peepers’ are used.
- Several good bits, each with a centrally placed germinating eye can be cut from an unbunched rhizome after trimming the roots.
- Selection of appropriate mother plant for raising new propagules either through in vivo or in vitro methods is important.
- About one kilogram uniformly sized rhizomes or bits, well-trimmed around the growing sprout are the best starting material.
- In some parts of India rhizomes are sun dried for 2-3 days after paring and pralinage treatment (trimmed of all roots, dipped in mud slurry and sprinkled with nematicide) and stored in shade for a week before planting.
- Non-availability of disease free uniform suckers,
- High pathogen (virus and nematode) attack at seedling stage
- High mortality in the field during establishment due to excessive flood irrigation,
- Long gestation period and Low yield.
The reasons behind all these problems can be attributed to the non-availability of disease free quality planting material and lack of hi-tech farming awareness among the growers.
Mass propagation of disease-free high yielding clones to produce consistently uniform and true to type plants by tissue culture is the only alternative for banana plantations.
Tissue culture technology :-
Tissue culture is the current technology that is applied for mass production of superior grade planting material for most of the crops. It is widely used to create clone plants of mother plant. This technology utilizes any part of the plant, viz., leaf, stem, root suckers, etc. for regeneration of a complete whole plant.
The process consists of some basic steps: Selection of mother plants, Culture Initiation, Multiplication of shoots initiated, Rooting of shoots, Primary Hardening in green houses and Secondary Hardening in shade houses and finally field transfer of tissue cultured plants.
Strict adherence to aseptic standards and micro-climatic conditions and care during the hardening process alone can ensure success.
General Steps Involved-
The banana tissue culture process involves the following steps:-
- Selection of mother plants. Healthy mother plant free from disease and pest should be selected.
- Mother plant should be true to type.
- Mother nursery must be located away from other banana plantations with an isolation distance of 500 m to maintain purity.
- Individual plants should be tagged with a code so that the tissue cultured plants could be traced back to the mother plant.
- Pedigree record and source of each mother plant should be maintained in a register daily.
- Initiation of aseptic cultures from explant obtained from disease-free banana plants.
- Multiplication of shoots in vitro.
- Induction of roots to individual shoots.
- Primary & secondary hardening of the tender plantlets in the polyhouse.
- Field transfer of the hardened tissue culture plants.
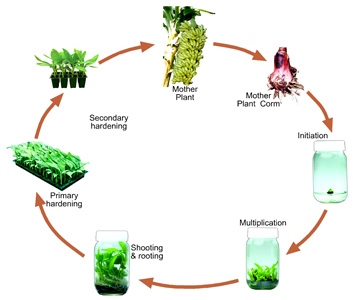
Stages of tissue culture of banana


Tissue cultured banana plant Tissue cultured banana plant for hardening
Advantages of tissue culture raised banana plants :-
- True to the type of mother plant.
- Better establishment in the field due to accelerated growth and well developed root system for better absorption of nutrients.
- Infection free planting material (Pest free, Disease free and Virus free).
- Uniform growth of all the plants unlike plants cultivated using suckers. So minimum number of harvests that reduces the cost and scope for getting a uniform ratoon crop.
- Optimal yield is ensured following proper cultural practices.
- Shorter harvesting period (Earlier maturity of crop) enables flexibility in accordance with planting season and marketing demand. Because of shorter crop duration of crop, two successive ratoons are possible with reduced cost of cultivation and increased profits.
- Large quantities of healthy and uniform plants can be supplied at a time round the year.
- 95 to 98% plants bear bunches.
- High benefit to cost ratio ensure good profits.
Cost economics of tissue cultured plant and sucker:-
Tissue cultured banana plant grown by the farmer wil give him lots of benefits which will ultimately result in higher profit than through traditional cultivation system. The tissue cultured plants show synchronized growth of plants with flowering and harvesting of banana.
Also the variation in non-fruit plants and off-type plants will not be there because of true to type plants. The quality of fruits are also improved and harvesting of three crops within 36 months an be possible with harvesting of 99% plants. It also increases average productivity by more than 60%.
So these benefits ultimately encourages farmers to adopt banana cultivation using tissue culture raised planting materials. The cost economics shown in table 1 clearly shows that tissue cultured banana cultivation will give farmer more profit as compared to the sucker propagated banana.
Table 1. Income from tissue-cultured and sucker-propagated bananas
| Particulars | Tissue cultured banana | Sucker Propagated Banana |
| Mean yield (bunches/ha) | 2663 | 2416 |
| Mean price received (Rs/bunch) | 94.47 | 76.42 |
| Value of main product (Rs/ha) | 251573 | 184630 |
| Value of by-product (Rs/ha) | 1729 | 2518 |
| Gross income (Rs/ha) | 253302 | 187149 |
| Total expenses (Rs/ha) | 141040 | 108294 |
| Net income (Rs/ha) | 112262 | 78855 |
| Cost of production per bunch (Rs) | 52.31 | 43.78 |
| Net income per bunch (Rs) | 42.16 | 32.64 |
| Source :- http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/58413/2/T-Alagumai.pdf | ||
Authors:
Arpita Mahobia, Shinde Umesh Dnyaneshwar and Zenu Jha
Dept. of Plant Molecular Biology & Biotechnology, Indira Gandhi Krishi Vishwavidyalaya , Raipur(C.G)- 492012
E mail id-
