भारत में एकल क्रॉस संकर के विकास के माध्यम से मक्का में किस्म सुधार
Maize (Zea mays L.) is the most widely distributed crop of the world being grown in tropical, sub-tropical and temperate regions up to 500 and from sea level to more than 3000m under irrigated to semi-arid conditions. Being a versatile crop, it adapts easily to a wide range of production environments.
In India, maize is the third most important cereal after rice and wheat that provides food, feed, fodder, and serves as a source of basic raw material for the number of industrial products,viz. starch, protein ,oil, alcoholic beverages, food sweeteners, cosmetics, bio-fuel, etc. No other cereal can be used in as many ways as maize. Virtually every part of the plant has an economic worth.
The grain can be consumed as human food, fermented to produce a wide range of foods and beverages, fed to livestock, and used as an industrial input in the production of starch, oil, sugar, protein, cellulose, ethyl alcohol, etc.
The leaves, stalks, and tassels can be fed to livestock, either green (in the form of fodder or silage) or dried (in the form of Stover). The roots can be used for mulching, incorporated into the soil to improve the physical structure, or dried and burned as fuel.
In India, maize is cultivated over 8.26 million ha with a production of 19.31 million tons having an average productivity of more than 2.4 tons/ ha, contributing 8.5 % to the Indian food basket. It occupies an important place as a source of human food (25%), animal feed (11%), and poultry feed (52%), starch (11%), brewery (1%) and seed 1% (Fig.1).
The growth rate of area (2.83 %), production (30.93 %) and productivity (27.35%) over the past years, has shown a remarkable increase as compared to other principal cereal crops. No other cereal crop has shown the high growth rate as of maize.
Maize breeding activities in India
Maize breeding strategy in India has gone through many phases of switch -over since the inception of All India Coordinated Research Project (Fig.2) on maize in 1957. However, the last three to five years have been the landmark years since the adoption of high yielding hybrids on farmers' fields proved as critical input for achieving high growth rate in maize.
The breeding activities have therefore, been re-oriented towards the development of high yielding single cross hybrids for different agro-ecological regions of the country seeing the strength of two-parent crosses for high yield and tackling the problems posed by biotic and abiotic stresses.
This has been duly supported by development of vigorous, productive and genetically diverse inbred lines that have good performance per se as well as in cross combinations.
Focus on Inbred-hybrid technology
The major mandate of AICRP (Maize) as well as DMR is to evolve and disseminate inbred-hybrid technology. With the urbanisation, specialty corn has gained a great acceptability among the masses. Their demand in Indian market has gone up. Sweet corn and baby corn hybrids/ varieties are sought to cater to the demands of peri-urban agriculture.
Over the years 131 hybrids have been developed and released since 1961; four dozen are public-bred single cross hybrids of different maturity ( extra-early, early, medium and late) and suitable for cultivation in different agro-climatic conditions of the country (zones 1 to 5, kindly see the Fig .2).
Since 2005, as many as 23 normal, seven Quality protein maize (QPM) and one each of baby corn and sweet corn single cross hybrids have been released. The detailed information on these hybrids including pedigree, characteristic features, area of adaptation, etc, has been provided in Table 1.
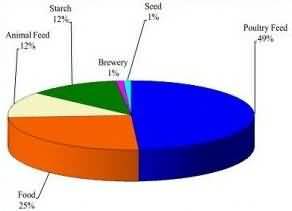
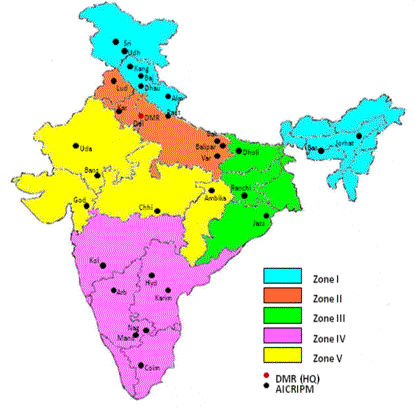
Table 1: Hybrids Developed and Released for Cultivation in India during last three years.
| Name | Pedigree | Centre / Year of release | Area of adoption | Characteristic features |
| NORMAL MAIZE | ||||
| DHM-117 | BML 6 X BML 7 |
ANGRAU, Hyderabad 2010 |
Andhra Pradesh | Medium,orange-yellow, flint, Nutrient responsive, tolerance to lodging & stay green,avg.yield 75q/ha |
| DHM-111 | BML 6 X BML 15 |
ANGRAU, Hyderabad 2010 |
Andhra Pradesh | Medium maturity,Yellow,semi-dent, Nutrient responsive, tolerance to lodging & stay green,avg. yield 65 q/ha |
| DHM-113 | BML 2 X BML 7 | ANGRAU, Hyderabad 2010 | Andhra Pradesh | Late,orange, semi-dent, Nutrient responsive & tolerance to lodging, avg.yield 66 q/ha |
| HM 11 | HK1-1128 X HK-163 | CCS HAU, Karnal 2009 | Across the country except Himalayan belt (rabi) | Late maturity, orange, flint, Responsive to higher doses of fertilizers, avg. yield 55 q/ha |
| HM10 | HKI 193-2 X HKI 1128 | CCS HAU Karnal 2008 | Delhi, Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and, Karnataka, | Medium maturity, yellow, semi flint, highly responsive to inputs, resistance MLB & avg yield 72 q/ha |
| PMH3 | LM 17 X LM 14 | PAU Ludhiana 2008 | Delhi, Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh | Late maturity, orange, flint, highly resposive to inputs & avg yield 75 q/ha |
| Nithya Shree | SKV-50 X NAI-105 | UAS Naganahalli 2008 | Karnataka (Kharif & rabi) | Late maturity,yellow-orange, semi-dent, resistant to lodging & avg yield 80 q/ha |
| Vivek hybrid 33 | V 372 X CM 212 | VPKAS Almora 2008 | Jammu & Kashmir and Uttarakhand | Early maturity, yellow, dent,avg. yield 50q/ha |
| Vivek 23 | V 351 X V 341 | VPKAS Almora 2007 | Hills of Uttaranchal | Early maturity, yellow, flint, bold, moderate tolerance against TLB, tall & avg yield 45 q/ha. |
| Maize PAU 352 | LM 15 X CML 32 | PAU Ludhiana 2007 | Punjab, Haryana, Delhi. | Early maturity, resistance to MLB, BSDM, ESR & avg yield 35-48 q/ha |
| HM 8 | HKI 1105 X HKI 161 | CCS HAU Karnal 2007 | Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu,, Maharastra, Karnataka | Medium maturity, orange, flint & avg yield 50-68 q/ha |
| HM 9 | HKI 1105 X HKI1128 | CCS HAU Karnal 2007 | Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa | Medium maturity, orange, flint & avg yield 60 q/ha |
| Malviya Makka 2 | HUZM 185 X HKI1105 | BHU Varanasi 2007 | East UP, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chattisgarh, West Bengal, Orissa | Medium maturity , yellow, semi flint, responsive to higher doses of fertilizers, resistance to MLB & avg yield 54 q/ha |
| COHM 5 | UMI 285 X UMI 61 | TNAU oimbatore 2007 | TN under irrigated & rainfed ecology | Late maturity, semi flint, responsive to high inputs, resistance to downy mildew, moderately resistance to stem borer, avg yield 42-55q/ha |
| PMH-1 | LM 13 X LM 14 | PAU Ludhiana 2007 | Irrigated areas of Punjab | Late maturity, stem is zig-zag, resistance MLB, stalk rots, avg yield 52q/ha |
| Vivek 21 | CM 212 X V 341 | VPKAS Almora 2007 | Uttaranchal, HP, J & K and NEH regions, Delhi, Punjab, Haryana & western UP, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu,, Maharastra & Karnataka | Extra early maturity, yellow, semi flint, bold, , tolerance against TLB & avg yield 45-50 q/ha |
| Vivek 25 | V 341 X V 346 | VPKAS Almora 2007 | Uttarakhand, HP, J&K and NEH region | Extra-early maturity, yellow, semi dent, bold, tolerance against TLB & avg yield 50-55 q/ha |
| Vivek 27 | V 335 X V 345 | VPKAS Almora 2007 | Eastern UP & Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, Chattisgarh, & WB & Maharashtra, AP, Karnataka, & TN | Extra early maturity, yellow, semi-dent & avg yield 50-55 q/ha |
| PMH-2 | LM 15 X LM 16 | PAU Ludhiana 2006 | Delhi, Haryana, Central & Western UP | Early maturity, short duration, resistance to MLB, BSDM, & PFSR |
| Buland | LM 11 X LM 12 | PAU Ludhiana 2005 | Punjab, UP, Haryana, Delhi, Tarai regions of Uttranchal. | Late maturity, resistance to TLB, Common rust, avg yield 85q/ha |
| HM 5 | HKI 1344 X HKI 1348-6-2 | CCS HAU Karnal 2005 | Haryana | Medium maturity, white, dent responsive to high doses of fertilizers, medium tall, tolerance to frost & avg yield 68-72q/ha |
| Vivek Hybrid Maize 15 | CM 152 X CM 212 | VPKAS Almora 2005 | J & K (Himalayan region), Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Maharastra & Karnataka | Extra early maturity with moderate degree of tolerance against TLB & avg yield 45-50 q/ha |
| Vivek Hybrid Maize 17 | CM 153 X CM 212 | VPKAS Almora 2005 | Across the country, except hill states. | Extra early maturity with moderate degree of tolerance against TLB, MLB, avg yield 40-50 q/ha |
| QPM (Quality Protein Maize) | ||||
| HQPM4 | HKI-193-2 X HKI 161 | CCS HAU Karnal 2010 | Across the country except Himalayan belt (rabi) | Late , yellow, semi-dent, avg. yield 60 q/ha |
| HQPM -7 | HK1-193-1 X HKI-161 | CCS HAU Karnal 2008 | Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka , Maharashtra | Late maturity, Yellow, semi-flint, Resistance to MLB, avg. yield 72q/ha |
| Vivek QPM - 9 | VQL1 X VQL2 | VPKAS Almora 2008 | Jammu & Kashmir and Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka , Maharashtra | Extra early maturity, yellow, dent, performed better at low N2 & avg. yield 52q/ha |
| HQPM 5 | HKI 163 X HKI 161 | CCS HAU Karnal 2007 | Across the country | Late maturity, orange, flint, responsive to higher doses of fertilizers, resistance to MLB & chilo partellus & avg yield > 58 q/ha |
| Shaktiman 3 | CML 161 X CML 163 | RAU Dholi 2006 | Bihar | Late maturity, orange-yellow, semi flint, tall, QPM hybrid with 0.73% tryptophan in protein, fair tolerance against MLB, LSM |
| Shaktiman 4 | CML 161 X CML 169 | RAU Dholi 2006 | Bihar | Semi flint, QPM hybrid 0.930 tryptophan in protein, , resistance against MLB. |
| HQPM 1 | HKI 193-1 X HKI 163 | CCS HAU Karnal 2005 | Across the country | Late maturity, yellow, dent, responsive to higher doses of fertilizers, tolerance to frost/ cold, resistance to MLB and common rust & average yield 62 q/ha |
| Baby corn | ||||
| HM 4 | HKI 1105 X HKI 323 | CCS HAU Karnal 2005 | Haryana, Delhi, Punjab, & Eastern UP | Baby corn, medium maturity, orange, flint, medium tall, , tolerance to frost & cold & avg. yield 60-68 q/ha |
| SWEET CORN | ||||
| HSC1 | HKI1831 X HKISC1 | CCS HAU Karnal 2010 | J&K, Uttarakhand | Medium, light yellow, Brix value >23 %, Avg. green ear yield 120 q/ha |
Authors:
J. Kaul, R. Sai kumar and Sain Dass
Directorate of Maize research, Pusa Campus, New Delhi 110 012
Email:
