सूरजमुखी: सूखा प्रवण क्षेत्रों के लिए पसंद की वाणिज्यिक फसल
Sunflower is one of the important crops in India's oil seed production that has contributed to rapid growth in oilseed production during late eighties and early 1990s. Sunflower is the oil of preference among the consumers' world over due to its health appeal. Sunflower is also a crop of choice for farmers due to its wider adaptability, high yield potential, shorter duration and profitability.
Sunflower also scores favourably against the traditional cultivated crops like rabi Jowar, Bajra, Castor and Pulses during the late Kharif/early rabi season due to following advantages.
- Short duration (80-115 days)
- Suitability to grow in rainfed conditions. The areas of Rayalseema, Marathwada and Karnataka are mainly rainfed and hence the drought tolerant capabilities of some hybirds like PAC-36 of Advanta India do provide the farmers in these areas with a better option.
- Ability to perform in diverse agro-climatic and soil conditions. The incidence of pests and diseases on Sunflower crop is also easily manageable with timely preventive and curative measures. The only major investment the farmer makes is the cost of hybrid seed.
- Sunflower, being a commercial crop, offers attractive price for the produce and the economics of the crop is highly profitable compared to other crops in similar maturity groups.
The farmers can substantially increase their income from Sunflower by paying attention to the following important cultivation aspects.
Selection of the right sunflower hybrid is critical as the final income is dependant on both grain and oil yields. As not all hybrids available in the market maximise both grain and oil yields, farmers need to be cautious while choosing the hybrids. In this aspect, it is appropriate to mention that some of the hybrids like PAC-36, PAC-8699 and PAC-1091 provide both high grain and oil yields. These hybrids, which are also notified by the government, have potential to yield upto 10 quintals/acre with oil content of >40%, under right growing and management conditions.
 2. Time of Sowing and Duration of Hybrid
2. Time of Sowing and Duration of Hybrid
- Farmers need to give very careful consideration to the time of sowing and based on which hybrids of right duration are to be selected. Longer duration hybrids (>95 days) are to be sown in the early season while medium-short duration hybrids (85-95 days) give better results, if sown later.
- Sunflower should be sown in 1st week of July, first fortnight of October and last week of January to 1st week of February during kharif, rabi and summer seasons respectively for obtaining higher yields of groundnut and sunflower in 6:2 and sunflower and red gram in 3:3 row proportion is found remunerative.
- Growing sunflower after sunflower should be avoided as it increases pest and disease complex and depletes the soil resulting in low yields.
- Spacing at 45 x 22.5 cm with one lakh plant population per hectare for variety Morden and 45 x 30 cm with seventy five thousand plant population for hybrid variety should be followed in Sunflower for higher yields.
3. Plant Nutrients
- Better yields in sunflower can only be realised by applying recommended dosage of fertilisers. Particularly, of importance are, application of phosphorous, potash and micronutrients like sulphur and boron. These nutrients, apart from improving plant health and increasing grain yields, also help in improving grain weight and oil content.
- A dose of 40:40:0 kg NPK/ha for Morden and 60:60:0 kg NPK/ha for remaining varieties/hybrids of sunflower should be applied for optimum yields. Potash @ 40 kg/ha should be applied in deficit soils. Nitrogen should be applied in two equal splits at sowing and 35 days after sowing.
- Application of 60 kg phosphorus/ha through Single Super Phosphate at sowing time increases seed and oil yield in sunflower.
- Application of 30 kg N and 30 kg P205/ha at sowing and three foliar sprays at 30, 40 and 50 days after sowing with Diammonium Phosphate + Urea (15 g Urea + 5 g DAP in one litre of water) increases the sunflower yield and reduces the cost on account of top dressing of fertilizers. Application of fertilizer and thinning are most important amongst improved package of practices in Sunflower.
4. Irrigation/rainfall
- Soil moisture, if available in adequate measure, during critical stages of vegetative growth, flowering and seed setting enhances grain and oil yield.
- Sunflower crop requires 9-10 irrigations during summer at an interval of 10-12 days in Feb., 8-10 days in March, 6-8 days in April & 4-6 days in May depending upon soil type.
5. Pest and Disease Management
Entomology
- It is decided that Economic threshold Level for Leaf hopper on Sunflower is 3 nymphs/leaf.
- For the management of leaf hopper spraying of Dimethoate 0.03% (10ml) or Methyl Demeton 0.03% (12 ml) or Monocrotophos 0.05% (14ml) or Formathion 0.03% (12ml) or Fenthion 0.05% (10ml)in 10 lit of water or Dusting of Malathion 5% or Methyl parathion 2% or Carbaryl 5% or Endosulphan 4% or phosalone 4% dust @ 20kg/ha is recommended.
- Use of nitrogenous fertilizers should be as per the recommended dose to reduce incidence of leaf hopper.
- For management of Helicoverpa and Spodoptera spraying of Phosalone 35 EC (14ml) in 10 litres of water or dusting of Carbaryl 10% dust @ 20kg/ha is recommended.
- For the management of mealy bug on sunflower spraying of dichlorovos 76% WSC @ 20 ml or methomyl 40 SP @ 10g + 20 g soap powder in 10 liter of water as soon as the pest incidence occurs and if needed second spraying is recommended.
- For management of whitefly and thrips on sunflower treatment with imidacloprid 70 WS @ 5 g/kg seed OR two spraying of Azadirachtin 1500 ppm @ 20 ml / 10 lit. of water at 15 and 30 days after emergence is recommended.
Plant pathology
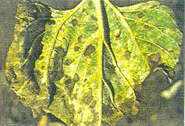
- Foliar diseases of sunflower caused by Alternaria, Curvularia and Bacterial leaf spot should be controlled by spraying Dithane M-45 0.25% three times at an interval of 15 days, starting first spray from the appearance of any leaf spot disease.
- Fungicidal seed dressing of Brassicol, Captan, Thirum or Bavistin @ 2 to 3 g/kg of sunflower seed was found to improve germination, plant stand and yields by protecting crop from seed and soil borne diseases.
- For controlling sunflower necrosis disease it is recommended that seed treatment with imidacloprid 5g/kg of seed before sowing and two spraying with imidacloprid 0.05% (5.0 ml in 10 litre of water) at 30 DAS and 45 DAS in crop growth period.
Authors:
Chanchala Rani Patel1, Dr. S.P. Singh2, Shri K. K. Painkra3 and Dr. Ashutosh Dubey4
1Farm Manger, 2 Programme Coordinator, 3Subject Matter Specialist(Agronomy) and 4Subject Matter Specialist (LPM)
Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Boirdadar, Raigarh, Chhattisgarh
Email: