मुगा रेशम उत्पादकता में सुधार के लिए मुगा रेशम कीट के मेजबान पौधे (सोम) मे रोग व कीट प्रबंधन
Sericulture is a viable cottage industry catering to the economically small and marginal families and hence this enterprise is well. accepted as an instrument for rural development.
India has the unique distinction of being the only country in the world producing all the four varieties of natural silk viz. mulberry, tasar, eri and muga on a commercial scale. Among them, Antheraea assamensis, (Helfer) bears special significance for production of golden yellow muga silk which is endemic to North East India.
The muga silkworm is a multivoltine and polyphagous insect. Som (Persaea bombycina Kost) and Soalu (Litsea monopetela (Roxb.) Pers are the primary food plants of muga silkworm (Choudhury, 1970). Som leaves improves silk producing ability where as, soalu leaves enhances egg laying capacity of muga silkworm (Thangavelu, et. al. 1986). Som plants grow up to an altitude of about 600 metres while Sualu up to 1000 metres above sea level.
 The nutrition of silkworm entirely depends upon the quality of leaves. The food plants (Leaves) have significant effect on health and survival of silkworms. Better the quality of leaves greater the possibility of obtaining good quality cocoons. Diseases make the leaf unpalatable for the silkworms and cause 6 -42% reduction in total leaf yield. Therefore knowledge on disease symptoms and its management is very important in muga industry.
The nutrition of silkworm entirely depends upon the quality of leaves. The food plants (Leaves) have significant effect on health and survival of silkworms. Better the quality of leaves greater the possibility of obtaining good quality cocoons. Diseases make the leaf unpalatable for the silkworms and cause 6 -42% reduction in total leaf yield. Therefore knowledge on disease symptoms and its management is very important in muga industry.
MAJOR DISEASES OF SOM PLANT
1. Leaf spot in Som tree
Causal organism
The causal organism is Phyllosticta perseae Ell. & Mart.
- Circular or irregular brown spots surrounded by yellow margin.
- Aappear on both surfaces of the young and mature leaves.
- As the disease progresses, the minute spots spread irregularly, become brown in colour.
- Form larger patches causing the drying up of the entire lamina and results in premature leaf fall.
Control:
- Morphotype S3 is less susceptible to leaf spot disease.
- Application of 0.1% Indofil M-45 twice at 15 days interval before the peak season of incidence insignificantly control the disease.
- Regular cultural operations, pruning and pollarding also prevent the disesse.
2. Anthracnose disease in Som tree
The Causal organism is Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz..
- Appears on young and mature leaves in the form of brown colour, round to oval spots.
- Irregularly spread to the entire leaf.
- As the disease progresses, the spots got collapsed and malformed.
- The infected areas dries up and become brown to black in colour.
- At the advanced stage of disease development, brownish colour (stromatic masses or sclerotia) lesions / streaks appears on the twigs also.
- The top of the branch or the entire brunch may wither away.
Control : :
- Plucking and burning of infected leaves at the initial stage can minimize the pathogen.
- Deep hoeing is an effective means to destroy the pathogen inoculam.
- Timely pruning and utilization of the leaves can prevent the disease.
- Moreover, destruction of the plant debris checks the secondary infection.
- Indofil M-45@ 0.01% can control the leaf blight disease.
3. Grey blight of Som tree
Pestalotiopsis desiminata (Thuem.) Stey is the causal organism of grey blight disease.
- The disease first shows its appearance as small, oval, discoloured lessons which are irregularly scattered on the leaves.
- The “ash” or grey colour spots grow irregularly with increasing of the infection.
- Symptom appears on both young and mature leaves.As the disease development progresses, the spots get collapsed, malformed and ultimately the entire leaf dries up.
Control:
- Timely cultural operation, pruning and pollarding can prevent the disease.
- Foliar spray of 0.1% Bavistin twice in 15 days interval can check the disease up to 85.2%.
4. Red rust of Som tree
Cephaleuros parasiticus Karst. is the causal organism of the disease.
- Appear as yellow green, orange or gray colour hairy pustules mostly on the upper surface of the leaves.
- The pustules are circular or irregular in shape and surrounded by chlorotic halos.
- Several large rust pustules coalesce to cover a large area of the leaf blade.
Control :
- Pruning and plucking of infected plant parts and leaves help in reducing the disease spread.
- Timely intercultural operations and utilization of the leaves can prevent the disease.
- Application of optimum dose of potasic fertilizers also helps in containing the disease.
- Spraying of 1 % Bordeoux mixture is general protective measure.
MAJOR DISEASES OF SOALU
1. Red rust in Soalu plant
 Cephaleuros parasiticus Karst. is the causal organism of the disease
Cephaleuros parasiticus Karst. is the causal organism of the disease
Symptoms:
- Yellow green, orange or gray colour hairy pustules on the upper surface of the leaves.
- The pustules are circular or irregular in shape and surrounded by chlorotic halos. Several large rust pustules coalesce to cover a large area of the leaf blade.
- The affected branches become stunted and bear fewer chlorotic leaves.
Control :
- Pruning and plucking of infected plant parts and leaves help in reducing the disease spread.
- Timely intercultural operations and utilization of the leaves can prevent the disease.
- Application of optimum dose of potasic fertilizers also helps in containing the disease.
- Spraying of 1 % Bordeoux mixture is general protective measure.
2. Brown blight in Soalu tree:
The Causal organism is Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz.
- Appearance of roundish to irregular brown spots on young and mature leaves in the form of ‘ash’ colour, round to oval spots irregularly spread to the entire leaf.
- As the disease progresses, the spots ,turning to grayish colour.
- The spots got collapsed and giving a blighted appearance.
Control:
Plucking and burning of infected leaves at the initial stage can minimize the pathogen.
- Timely pruning and utilization of the leaves can prevent the disease.
- Phyto-blighton A bio formulation which act as fungitoxic to plant pathogens an anti fungal bio-product developed by Plant Pathology Laboratory of CMERTI, Lahdoigarh
MAJOR PESTS OF MUGA HOST PLANTS
- The caterpillar feeds the tissue of the trunk and make bores into the main trunk.
- The number of holes per plant is ranges between 1 - 5 and size of holes are 0.5 – 2.0 cm.
Control:
- Plugging of stem borer holes with cotton ball soaked in 5-15% plant extract of Neem, Dotura , Titabahak and Castor can be controlled up to level of 80% infestation.
- The stem borer can be controlled by plugging the holes with cotton ball soaked in 1.5% chemical, Nuvan solution followed by mud plastering.
2. Leaf gall infestation in Muga host :
Gall is malignant tumor like growth induced by toxic saliva secreted by gall insect
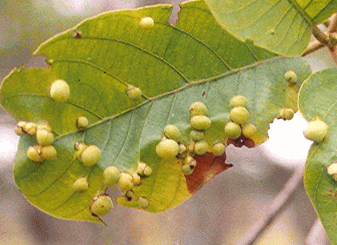
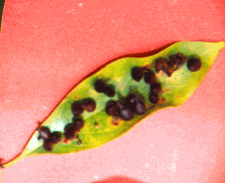
Control:
- Severally gall infested plants should be pollarded and all the gall infested leaves and branches should be destroyed through burning.
- The low infested leaves should be plucked and burned to minimize further multiplication.
3. Cricula pest in Muga host:
 Locally known as ‘Amphutukani’ in Assam. The larvae of the pest voraciously fed leaves of som plant causing drastic loss of foliage.
Locally known as ‘Amphutukani’ in Assam. The larvae of the pest voraciously fed leaves of som plant causing drastic loss of foliage.
Control:
- The pest can be control mechanically by collection and killing of caterpillar and eggs.
- Cocoons should be collected and burned to stop further mulplication. In chemical control, 0.05% phosphamidon is used effectively to control the pest.
MODERATE PESTS OF MUGA HOST PLANTS
1.  Leaf roller of Muga host plant:
Leaf roller of Muga host plant:
- This is occasional severe pest of soalu plant.
- The developing larvae of the pest secrete gummy substances and roll the adjacent leaves forming roll of leaves.
Control:
- Mechanical control though plucking and burning of infested leaves effectively reduce incidence of leaf roller.
2. Shoot borer of Muga host:
 It is common pest of muga host plant
It is common pest of muga host plant
CONTROL:
- Mechanically by burning and destroying of infested shoots is found effective.
3. Leaf minor of Muga host :
It causes extensive damage of the leaves of the plants by destroying the epidermis by tunneling in the leaves.
CONTROL:
- Mechanical control though plucking and burning of infested leaves effectively reduce incidence of leaf minor.Spraying 0.2% Rogor after 15 days interval controls the pest.
4. Aphids infestation in Muga host :


- Aphids cause damage to developing buds in terminal branches of som and soalu.
- Both nymph and adult insect remain in colonies and preferred to suck saps from the bud, lateral surface of the tender leaves and shoots of the plant.
- Continuous de-sapping resulted in leaf curling and reduction in size of the leaves. Honeydew secretion of aphids facilitates growth of saprophytic fungus causing growth of black sooty mould on the leaves.
Control:
- Destroy and burning of infested parts of the plant,
- To avoid closer spacing, selection of shady area for raising nursery to prevent the pest infestation.
- Entomophagous insect which are voracious feeder on aphids can be used as biological control.
Authors:
Ranjana Das
Central Muga Eri Research & Training Institute (CMER&TI),
Lahdoigarh, Jorhat-785700, Assam, India
Email:







