आलू मे प्रजनक बीज उत्पादन
Breeder seed is seed or vegetative propagating material directly controlled by the originating or sponsoring plant breeder of the breeding programme or institution and/or seed whose production is personally supervised by a qualified plant breeder and which provides the source for the initial and recurring increase of foundation seed.
Breeder seeds are produced using nucleus seeds in the Research institutes or Universities under the supervision of a breeder. The entire production process will be monitored by the Scientists and Officers of the Seed Certification Department and by the representatives of the National Seed Corporation.
The genetic purity of the breeder seeds is 100% and the tag provided for the breeder seed is golden yellow in colour. Breeder seed shall be genetically so pure as to guarantee that in the subsequent generation i.e. certified Foundation seed class shall conform to the prescribed standards of genetic purity.
The other quality factors of Breeder seed such as physical purity, inert matter, germination etc. shall be indicated on the label on actual basis.
Importance of quality seed in potato
High yields of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in the field like other crops revolves around use of high-quality seed potatoes. Since potato is a vegetatively propagated plant, fungal, bacterial and especially viral diseases easily affect seed tubers. Viral diseases are mainly responsible for degeneration of seed tubers, which decrease their vigor as well as productivity.
Since, the crop is multiplied vegetatively using tuber as seed; it gets degenerated very fast necessitating replacement after every four years. Additionally, the seed is either unavailable or out of the reach of poor farmers owing to high seed cost.
The seed related issues are further aggravated due to restricted accessibility to seed producing regions, transportability of quality seeds. Quality seed can the increase in yield by 15 - 20%.
At present the country has an area of approximately 2.14 million ha under potato and as such requires about 6.42 million tones of quality seed at the rate of 3-3.5 t/ha to achieve 100% seed replacement rate.
Every year, the desirable seed replacement rate of 25% is must to get good production and productivity of potato in the country. However, the current average seed replacement rate of potato in India is much below than the desirable seed replacement rate (25%).
The ICAR-Central Potato Research Institute (CPRI) is the backbone of the formal seed production in India and develops the breeder seed by conventional (tuber indexing and clonal selection) and hi-tech seed production system (micro-propagation).
CPRI is collaborating with other state agricultural universities and private seed companies to augment the production of breeder seed of important varieties to meet out increasing seed demand in the country.
Stages of breeder seed production
Breeder seed in potato produced from nucleus seed. The nucleus seed is developed in the hills produced during long day conditions at a temperature range of 12-28oC and 8-28oC in plains.
The nucleus seed can be developed either through clonal selection and tuber indexing and after ELISA testing for viruses, diseases free tubers are multiplied in the field in stage-I at a spacing of 1 x 1 m in hills and 1.2 x1.0 m in the plains.
The produce of stage I is further multiplied in stage II at a spacing of 1.0 x 0.2 or 1.2 x 0.2 m in hills and plains respectively. The seed produced in these stages is called nucleus seed.
Under hi-tech system by micropropagation through meristem tip culture and hardened microplant, microtuber and aeroponic minituber planted in nursery beds in mixture of soil, sand and FYM (2:1:1) in rows at 30 cm × 10 cm spacing under insect proof net house condition.
Minitubers harvested (Generation-0) are called as nucleus seed. Stage II seed tubers and Minitubers (Generation-0) will be planted in the field during next season in 60x20 cm spacing for production of (pre breeder seed ) Stage III and generation 1. Stage-III and generation -1 seed tubers respectively which are further multiplied for production of breeder seed (Stage-IV/Generation-2).
Basic requirement for breeder seed potato production
Agro climatic conditions
There are two seasons of seed production in the country i.e. summer and autumn. In summer season, seed production is done under long day and rain fed conditions in high hills from February to October
In autumn season the seed production is done in sub-tropical plains under short day and irrigated conditions from October to March. The adverse weather conditions from land preparation to harvesting and storage largely affect the yield and seed quality.
Potato is a low temperature crop and grows well between 12 to 28 oC in hills and 8-28 oC in the plains. The optimum temperature is 18-22 oC for foliar growth while the lower temperature 10-16 oC is good for tuberization and bulking of the crop.
The crop is grown under long days in the hills. A minimum photoperiod of 8-10 hours is necessary for optimum yields under short day conditions in the plains. The sunshine shorter than 8 hours will adversely affect the seed potato production.
In Potato Aphid Viruses get transmitted through contact or insect vectors (aphids and thrips) and cause infection in the crop. Hence 75 days should be aphid free period is required during growing season (fig 1). On the basis of aphid free period, the breeder seed production zones are given below
Table 1. Suitability of regions for breeder seed production
| State | Zone | Type of seed | Remarks |
| Himachal Pradesh | North high hills | Nucleus, Breeder, Foundation and Certified seed | Low aphids during cropping season and no serious soil and tuber borne disease and pests |
| Jammu & Kashmir | Northern high hills | Breeder seed, Foundation and Certified seed | Low aphid infestation |
| Punjab, Haryana, UP,MP, Bihar | Indo-Gangetic plains | Nucleus, Breeders, Foundation and Certified seed | Low aphids during October to mid-January and no serious soil and tuber borne diseases |
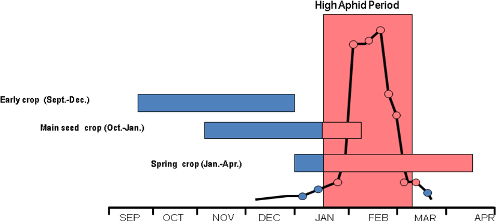
Fig 1 Low aphid population in subtropics
Rain fall and irrigation
Regular rains at interval of 10-12 days is desirable in hills before monsoon to avoid drought which delays tuberization. In plains sufficient availability of water for frequent irrigation (7-8 times at an interval of 6-8 days) is essential for better growth and tuberization.
Soils
Potato grows well at pH 5.5. to 8.5 in sandy loam, sandy and clay loam soils but the best soil is with pH 6.0 to 7.0. In hills, soils are slightly acidic. Sandy loam and loam soils are best as the root system and stolon penetrate easily in the soil. In sandy soils the penetration of roots and stolons is easy and the tuberization occurs earlier and leads to early maturity of crop while in clay loam soil they are delayed.
Manures and fertilizers
Potato being fertilizer responsive crop, manures & fertilizers are the important inputs that affect its yield.
Manure: Potato requires well rotten 10 to 15 t/ha FYM if green manure crop is taken otherwise 30 t/ha FYM is to be applied.
Fertilizers: The crop requires balanced use of NPK for optimum production. NPK fertilizer doses for (stage IV) breeder seed are required as given in Table-2. Fertilizers recommended for are ammonium sulphate, single super phosphate (SSP) and muriate of potash (MOP).
Half dose of N and full doses of P & K should be applied before planting. High dose of nitrogen than recommended one will mask the virus symptoms in the crop hindering the rouging of virus infected plants. FYM and fertilizer (CAN, SSP & MOP) can be applied simultaneously at planting.
Table 2: Recommended dose of fertilizers
| Stage | Nitrogen (Kg/ha) | Phosphorous (Kg/ha) | Potassium (Kg/ha) |
| Hills | |||
| Breeder seed | 120 | 100 | 100 |
| Plains | |||
| Breeder seed | 150 | 60 | 100 |
Healthy seed
The healthy pre breeder seed (Stage-III) free from viral, bacterial diseases and nematodes is used for breeder seed produuction.Varietal purity, size of tubers (40-50g), right physiological conditions and disease freedom collectively determine the quality of seed.
Laboratory and equipment facilities
They are essential to carry out serological (ELISA) testing for virus detection.Testing of 150 plants/ha in breeder seed done randomly as per procedure of ELISA testing.
Breeder seed production under Seed Plot Technique (SPT)
The technique, of growing seed potato crop during low aphid period with healthy seed from October to first week of January coupled with the use of insecticides, rouging and dehaulming in the last week of December or up to second week of January was developed by the ICAR-CPRI, Shimla in 1959 and is called as “Seed Plot Technique”.
Quality seed production was possible under this technique in sub-tropical plains by advancing the date of planting from December end to first week of October. Breeder seed is produced at ICAR-CPRI regional centres with seed plot technique under strict supervision of scientist (fig 2).
The produce of pre breeder seed in III and Generation-1 further multiplied following SPT in 4th year in stage IV and third year in Generation-2 at a normal spacing of 60 x 20cm called as breeder seed.
The breeder seed is internationally called as basic seed but in India the farmers and Government officials are more acquainted with the term breeder seed so the term breeder seed is used in the text.
Characteristic features of SPT
- There should be a low aphid or aphid free period of 75 days after the planting of crop.
- Adopt 2-3 years crop rotation to take care of soil borne pathogens.
- Seed crop should be grown in isolation of 25 meters from ware crop.
- Seed should be procured from reliable sources and must be free from viruses and soil borne pathogens. Cold stored seed of right physiological age should be used.
- Crop should be planted on 10thOctober in Punjab, 25thOctober in Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh and 5th November in Madhya Pradesh, Eastern Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
- Systemic insecticide such as Cartap hydrachloride to be applied in split doses of 20kg/ha at the time of earthing up against sucking insects.
- Pre-sprouted seed with multiple sprouts may be used, which ensures quick, uniform and early emergence.
- For weed control, use herbicides (metribuzin/sencor @ 750g/ha within 3-4 days of planting.
- Inspect the seed crop thrice at 45, 60 and 75 days during growing season to remove off type and virus infected diseased plants.
- Alternate spray of Imidacloprid @ 0.002%, triazophos @ 1.6 l/ha and thiamethaxam @ 130g/ha to protect seed crop from insects after emergence at 15-20 days interval.
- Spray the crop with mancozeb @ 2.0 kg/ha at 10 days intervals from 3rd week of November and spray Curzate M-8 @ 3.0 kg/ha as and when late blight is observed.
- Irrigation should be with hold in 3rdweek of December e. 7-10 days before haulms killing in north-western plains and 1stweek of January in north-eastern plains.
- Haulms killing to be done in the end of December in Punjab, Haryana, Western Uttar Pradesh; by 10th January in Central Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and by 15th January in eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar.
- Harvest the crop, 15-20 days after haulms killing when the fields are in workable condition and tuber skin is hardened. Cure the crop in heaps in a cool shady place for about 15-20 days.
- Treat the produce with commercial grade Boric Acid 3% solution for 20 minutes to prevent surface borne pathogens. Dry in shade and fill in bags, sealed and labelled properly before supply to different agencies for further multiplications.
Table 3.Breeder seed crop planting, dehaulming and harvesting schedule
| Location | Planting | Dehaulming | Harvesting |
| Punjab and Haryana | Oct. 7 | Dec. 31 | Jan. 15 |
| NW and central plains | Oct. 15 | Jan. 10 | Jan. 25 |
| Eastern UP and MP | Oct. 31 | Jan. 15 | Jan. 31 |
| Bihar | Nov. 7 | Jan. 20 | Jan. 31 |
Certification
Breeder seed will not be certified by seed certification agency (SCA). It will be monitored by monitoring team comprising of personal from production institute, seed certification agency representative and seed production agency representative.
Bagging: Seed should be weighed and bagged for sale or distribution depending on indent of client. There must be logo in bag mentioning name of producing institute and name of variety
Tagging/ labelling:
Golden yellow tag containing following information should be issued along with the seed. One tag issued in every bag
Size of label: 12 x 6 cm
Information on label: Breeder seed shall be supplied in sealed bags, duly stitched and sealed. A cloth-lined label of 12 cm x 6 cm containing following information shall be fixed on the container.
|
Crop Variety Class of seed Lot No. Date of test *Pure seed *Inert matter *Germination Producing Institution (name and address) |
Breeder seed
% % %
|
Label No. |
*Based on actual.
Breeder seed performae to be submitted
- BSP-I: Allocation of breeder seed production
- BSP-II: Time table of production and availability of breeder seed
- BSP-III: Inspection report of the monitoring team
- BSP-IV: Breeder seed actually produced
- BSP-VI: Grow out Report
- BSP-VII: Breeder seed distribution
Seed Standards for potato breeder seed
There is no such standard for breeder seed as such but it should be such that the seed produced from it should meet foundation seed standard
- Genetic Purity : 100%
- Inert Matter: Nil
- Minimum Germination : 99%
- Specification in respect of size and weight of seed material shall be as under
| Size | Mean length and two widths at the middle of tuber | Corresponding weight |
| (a) Hill seed (HS)Seed sizeLarge size | 30mm-60mmabove 60mm | 25-150gm above 150gm |
| (b) Plains seed (PS) Seed size large size | 30 mm- 55 mm above 55 mm | 25-125gm above 125 gm |
Potato breeder seed indent and allotment
- Breeder seed indent shall be placed one year before requirement
- Each State in consultation with ICAR Institutes, SAUs and Seed producing Agencies shall formulate seed plan (for Breeder, Foundation and Certified Seed) for the cropping seasons on the basis of an assessment of existing and new varieties in terms of actual or potential yield in each district/agro-climatic zone.
- State Governments shall submit the seed plan and the Breeder Seeds indent to DAC/ICAR, for national varieties by 15th June for potato (Rabi crop- potato).
- Private seed companies will also place the breeder seed indent by 15th June for potato (Rabi crop- potato) through National Seeds Association of India (NSAI) to Seeds Division,DAC.
- DAC shall compile all the Breeder Seed Indents of States and private seed companies and furnish them to ICAR/ concerned PDs/PCs for production of the breeder seeds.
- The breeder seed will be allotted to all States and private seed companies for lifting from institutes of ICAR to produce foundation and certifiedseed
- Indent of breeder seed will be published on seednet portal (http://seednet.gov.in)
- The Lifting of Breeder Seed is to be monitored jointly by DAC and ICAR.
Potato breeder seed price
Every year price of the breeder seed will be decided by central government
| Year | Price (Rs/qt) |
| 2016-17 | 2800 |
| 2017-18 | 3500 |
| 2018-19 | 3500 |
| 2019-20 | 3500 |
| 2020-21 | 3500 |
Authors:
Murlidhar Sadawarti, SP Singh, RK Singh, Subhash Katare, Tanuja Buckseth, Shyam Kumar Gupta, RK Samadhiya, YP Singh, Sanjay Sharma and Surender Singh
ICAR–Central Potato Research Institute, RS Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh 474020
ICAR–Central Potato Research Institute, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh 171001
Email:
