भिण्डी की फसल में संकर बीज का उत्पादन करने की विधि।
Okra commonly known as ‘bhendi’ or lady’s finger is native of tropical Africa, Okra is widely cultivated in Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, Maharashtra, and Gujarat are important okra producing states of India. Okra belongs to family Malvaceae with 2n=8x=72 or 144 chromosomes and is polyploidy in nature. It is often pollinated crop.
Hybrid Seed Production of Okra
The most productive and desirable hybrid seed obtained from the female parent when there is a perfect coincidence of stigma receptiveness and pollen viability.
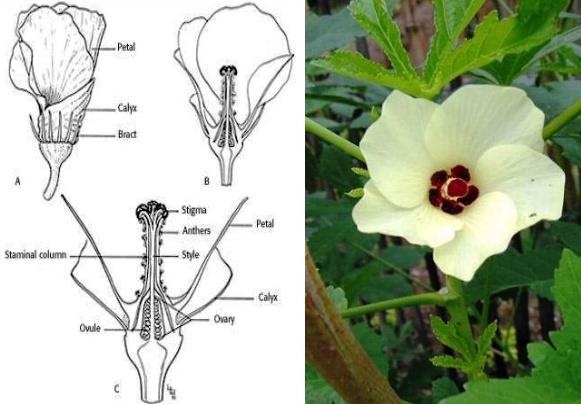
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from male parent to female parent is called as pollination. The just opened flowers were picked from the male parent in a separate brown paper pockets and used for crossing of emasculated flowers. Different colour thread was tied to the pedicel of the crossed buds for easy identification.
Pollination was carried out daily between 8-00 am to 4-00 pm. The crossing was carried out for a period of eight weeks from the initiation of flowering and avoid the selfed seeds in the hybrid. Therefore, time of pollination and ratio between female to male flower crossing is to be optimized to get increased seed set and yield in female parent of bhendi.
Materials requidred for Emasculation and Pollination
For emasculation of flower bud, forceps and needles are required, while plastic container, pollen ring, scissors and brush are needed for pollen extraction from anthers and for pollination work.
Emasculation
Removal of androecium (stamens) from bisexual flower is called as emasculation. The buds opened next day, were selected in female parent and emasculation was carried out by removing the androecium along with the corolla. These emasculated buds were covered with butter paper pockets to avoid cross pollination and also for easy identification of emasculated flower for pollination. The emasculation was carried out daily from 2-00 to 6-00 pm.
Land requirement
Field should be free from wild bhendi and crop was not grown in the previous season. The land was brought to the fine tilth by ploughing with mould board plough and repeated blade harrowing after the harvest of previous crops.
Varieties:- CO1, MDU 1, Parbhani Kranti, Arka Anamika, Pusa A-4, Pusa Sawani, jaya, Subha
Hybrids:- CO2 (AE 180 X PUSA SEWANI), CO3 (PRABHANI KRANTI X MDU1), Mahyco hybrid, Shoba and Prabhani kranti.
Field isolation requirement
The seed fields must be isolated from fields of other varieties and fields of same variety and from wild Abelmoschus species by at least 400 and 200 m for foundation and certified seed production respectively.
Cultural pracices
Sowing of okra seed crop:- Early kharif sown crop or summer sown crop is good for seed production. Sowing should be done in rows by following a spacing of 60 x 30-45cm for kharif season and 45 x 30 cm for summer season.
Seed rate:- Varieties : 8-10 kg/ha Hybrids : 8 kg/ha (Female) 4 kg/ha (Male).
Planting ratio:- For hybrid seed production, female and male parents are normally planted in the ratio of 8:1 in Block system.
Thinning:- The thinning operation was carried out by removing weak and diseased plants and maintaining only one healthy and vigorous seedling.
Weeding and inter cultivation:- Four hand weeding (at 30, 45, 60 and 75 DAS) were carried out during the crop growth period. Inter cultivation with entire blade hoes were carried out at an interval of 15 days starting from 20 to 30 days after sowing. The earthing up was done manually at 30 days after sowing.
Manuring
In Okra seed crop, apply 12.5 tons of FYM/ ha before ploughing. Apply 150:75:75 kg NPK/ ha, of which 50% of the N should be applied as top dressing in two split doses, one at flowering stage and another 10 days later.
Distance between Male and Female fields
There should be a distance of 5 metres between male lines and female lines

Rouging
The rouging should be based on the plant characters, hairiness, fruit character like fruit colour, number of ridges, fruit length etc., and the off type and mosaic attacked plants should be removed from the seed field. Wild bhendi if present should be removed before flowering.
Irrigation in Okra seed crop
Five to six protective irrigations are required for the whole crop period.
Field inspections
A minimum of three inspections shall be made, the first before flowering, the second during peak flowering and fruiting stage and the third at mature fruit stage and prior to harvesting.
Insects and Pests of Okra crop
- Shoot and fruit bore: (Earias sp)
- Fruit Borer: (Helicoverpa armigera),
- Sucking Pests -Jassids: (Amrasca biguttula biguttula) , Whiteflies: Bemisia tabaci , Green peach aphid: Myzus persicae, Ants
- Red Spider Mites
- Root-knot nematodes.
The major pest jassids, aphids and white fly, can be controlled by spraying Rogar or Dimecron or Endosulphon. The pod borer and red spider mites can be controlled by spraying Endosulphon and Kelthane, respectively.
Major diseases of Okra
- Okra Vein Mosaic Virus (YVMV) Causative agent: Yellow Vein Mosaic Virus ,
- Cercospora Leaf Spot Causative agent: Cercospora abelmoschi, C. Malayensis, C. hibisci,
- Fusarium Wilt Causative agent: Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Vasinfectum ,
- Powdery Mildew Causative agent: Erysiphe cichoracearum, Sphaerotheca fuliginea ,
- Root-decaying disease. Enation
- Leaf Curl of Bhendi ,
- Damping Off Causative agent: Pythium spp., Rhizoctonia spp.
The diseases such as yellow vein mosaic and powdery mildew can be controlled by spraying systemic insecticides and Karathane, respectively.
Harvesting and Threshing of Okra for seeds
The pods which expose hairline crack and turn to brown colour on drying alone are cut using sickle manually (30-35 days after crossing).


The pods are dried and threshed using pliable sticks . Separated seeds are winnowed to remove plant debris and dried over a tarpaulin to 10% moisture content. Dried seeds are subject to water floatation in which, good seeds sink while poor seeds float. The floaters are removed, while sinkers are dried under shade followed by sun drying. Then the seed are cleaned, dried and treated with Captan/ Thiram. Seeds are to be processed with BSS 7 wire mesh sieve.
Okra Seed Yield:- 1000-1200 Kg/ha
Authors:
MONIKA MEENA ANIL MEENA AND RAJANI VERMA
Department of Plant breeding and genetics, Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture and Technology, Udaipur -313001
Division of Entomology, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi-110012
Department of Plant breeding and genetics, S.K.N. College of Agriculture, Sri Karan Narendra agriculture University, Jobner-30329.
Email:
